CSV Scanner¶
Getting Started¶
As we utilize the Gunzip for decompressing the compressed CSV file and CRC32C for calculating the checksum, please make sure you download the whole package of Vitis_Libraries, otherwise the target will not be able to be built successfully.
To simplify the potential users integration efforts, we created a multithreaded test environment at L3/tests/gunzip_csv_sc_test and packed the Vitis System Compiler applicatoin layer in L3/src/sw/gunzip_csv, so that the users won’t need to take care of the detailed scheduling works.
Limitation¶
The CSV scanner kernel can be described as:
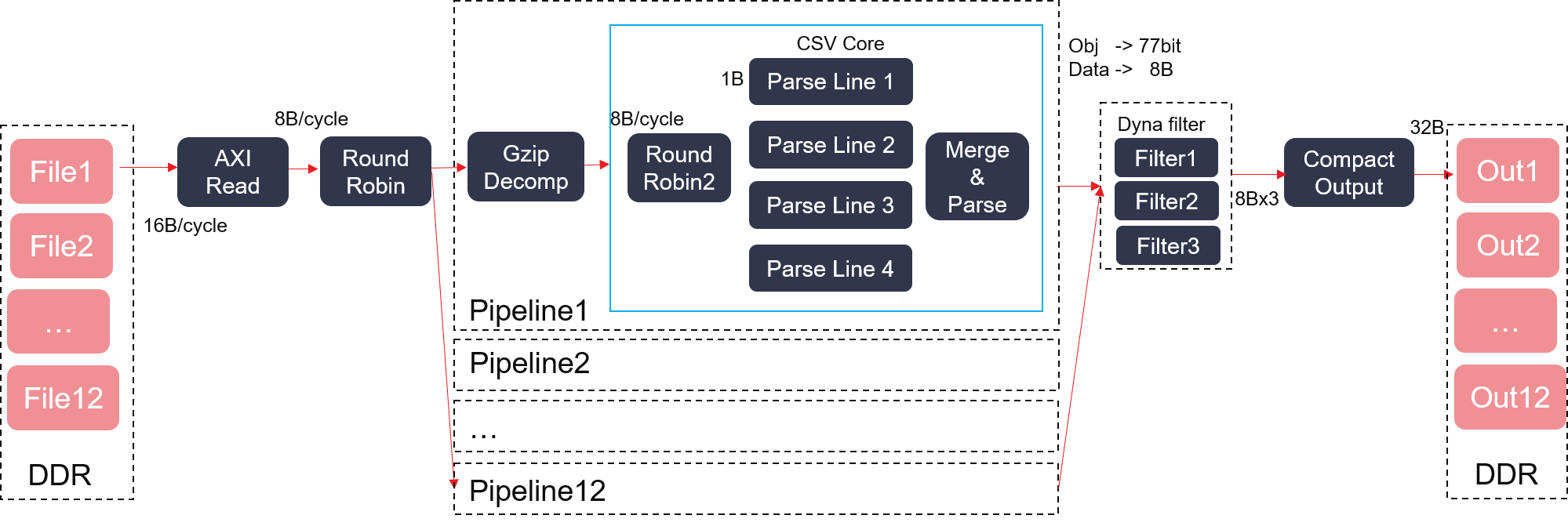
maximal number of input files: as we have only 12 processing units (PU) inside the kernel, the maximal number of input files should be limited to 12 at one call.
Data types: 5 data types are supported currently, including: int (64-bit), string (up to 1024 chars), date, bool, and numeric (56-bit significand, 8-bit exponent).
CSV format: up to 16 columns are supported, up to 8 columns post CSV parsing, and the length of one row should be less than or equal to 1024 bytes.
filter operator: only 7 types of operator are supported, the operators are listed below:
FilterOp Description FOP_DC don’t care FOP_EQ equal FOP_NE not equal FOP_GT greater than FOP_LT less than FOP_GE greater than or equal FOP_LE less than or equal
Example Usage¶
Let’s take TPC-H query-1 for example:
At first, you have to set up the schema for the input CSV files to let our engine knows the specific data type that each column is
// declare the scan description sssd_scandesc_t sd_q1; // set the schema sssd_schema_t schema; schema.natt = 16; sssd_dtype_t* dtype = (sssd_dtype_t*)malloc(sizeof(sssd_dtype_t) * schema.natt); dtype[0] = SSSD_DTYPE_INT; // l_orderkey dtype[1] = SSSD_DTYPE_INT; // l_partkey dtype[2] = SSSD_DTYPE_INT; // l_suppkey dtype[3] = SSSD_DTYPE_INT; // l_linenumber dtype[4] = SSSD_DTYPE_NUMERIC; // l_quantity dtype[5] = SSSD_DTYPE_NUMERIC; // l_extendedprice dtype[6] = SSSD_DTYPE_NUMERIC; // l_discount dtype[7] = SSSD_DTYPE_NUMERIC; // l_tax dtype[8] = SSSD_DTYPE_STRING; // l_returnflag dtype[9] = SSSD_DTYPE_STRING; // l_linestatus dtype[10] = SSSD_DTYPE_DATE; // l_shipdate dtype[11] = SSSD_DTYPE_DATE; // l_commitdate dtype[12] = SSSD_DTYPE_DATE; // l_receiptdate dtype[13] = SSSD_DTYPE_STRING; // l_shipinstruct dtype[14] = SSSD_DTYPE_STRING; // l_shipmode dtype[15] = SSSD_DTYPE_STRING; // l_comment schema.dtype = dtype; schema.ftype = "csv"; schema.u.csv.header = 0; schema.u.csv.delim = 0; schema.u.csv.quote = 0; // give the schema to the scan description sd_q1.schema = schema;
Secondly, you may want to specify which columns that you want to calculate the hash value by
// number of hashes sd_q1.nhashatt = 2; sd_q1.hashatt = (int32_t*)malloc(sizeof(int32_t) * sd_q1.nhashatt); // which column that need to be hashed sd_q1.hashatt[0] = 8; sd_q1.hashatt[1] = 9;
Then, you should choose which columns that should be given in the result buffer
// number of output columns sd_q1.natt = 7; sd_q1.att = (int32_t*)malloc(sizeof(int32_t) * sd_q1.natt); // which column that should be output sd_q1.att[0] = 4; // l_quantity sd_q1.att[1] = 5; // l_extendedprice sd_q1.att[2] = 6; // l_discount; sd_q1.att[3] = 7; // l_tax; sd_q1.att[4] = 8; // l_returnflag sd_q1.att[5] = 9; // l_linestatus; sd_q1.att[6] = 10; // l_shipdate;
For filtering the specific column, you should set up a filter like
// number of filter sd_q1.nfilter = 1; sssd_filter_t** filter = (sssd_filter_t**)malloc(sizeof(sssd_filter_t*) * sd_q1.nfilter); for (int i = 0; i < sd_q1.nfilter; ++i) { filter[i] = (sssd_filter_t*)malloc(sizeof(sssd_filter_t)); } // l_shipdate <= 19980902 filter[0]->att = 10; // l_shipdate filter[0]->dtype = SSSD_DTYPE_DATE; filter[0]->cmp = SSSD_LE; filter[0]->arg_value.cmp_date.year = 1998; filter[0]->arg_value.cmp_date.month = 9; filter[0]->arg_value.cmp_date.day = 2; // push the filter into the scan description sd_q1.filter = filter;
After all the setups, you may want to set callback and instantiate the multi-thread processing by
// set callback sssd_listfn_t fl = sssd_listfn; sssd_scanfn_t fn = sssd_scanfn; list_out_t list_ctxt = {0, 0}; list_ctxt.list_out = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * 1024); for (int i = 0; i < 1024; ++i) { list_ctxt.list_out[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 1024); } // Multiple thread test std::thread t1( [&sssd, &fl, &list_ctxt](const char* pattern) { int ret = sssd_list(sssd, pattern, fl, &list_ctxt); if (ret == -1) printf("list failed\n"); }, path_pattern); t1.join(); printf("fnm = %d\n", list_ctxt.fnm); std::thread t_pool[list_ctxt.fnm]; scan_out_t* scan_ctxt = (scan_out_t*)malloc(sizeof(scan_out_t) * list_ctxt.fnm); int t_nm = 36; if (list_ctxt.fnm < t_nm) t_nm = list_ctxt.fnm; for (int i = 0; i < t_nm; ++i) { // int ret = sssd_scan(sssd, list_ctxt.list_out[i], &sd_q1, fn, &scan_ctxt[i]); // if(i < list_ctxt.fnm) { t_pool[i] = std::thread( [&sssd, &sd_q1, &fn, &list_ctxt, &scan_ctxt](const int nm, const int id) { for (int j = 0; j < (list_ctxt.fnm + nm - 1) / nm; ++j) { int idx = j * nm + id; if (idx < list_ctxt.fnm) { scan_ctxt[idx].row_nm = 0; scan_ctxt[idx].sd = &sd_q1; char* file_name = list_ctxt.list_out[idx]; scan_out_t* ctxt = &scan_ctxt[idx]; int ret = sssd_scan(sssd, file_name, &sd_q1, fn, ctxt); if (ret == -1) printf("scan failed\n"); } } }, t_nm, i); } for (int i = 0; i < t_nm; ++i) { t_pool[i].join(); printf("output rows %d\n", scan_ctxt[i].row_nm); }
Finally, don’t forget to release the resources after the acceleration process done
// release resources free(sd_q1.att); for (int i = 0; i < sd_q1.nfilter; ++i) { free(filter[i]); } free(filter); free(sd_q1.hashatt);