Kernel Design¶
LZ Data Compression¶
Overview¶
Xilinx LZ data compression architecture is targeted for FPGAs. It aims to provide high throughput. This architecture is developed and tested on Xilinx Alveo U200. Even though this architecture is designed for the LZ4 application, it is generic enough to support various other LZ based data compression algorithms like Snappy, LZ77 and LZO.
Xilinx FPGA based LZ data-compression architecture contains multiple compression engines which run concurrently to get higher throughput. Each compression engine is designed to process 1 byte/clock cycle @300MHz. If the design contains N compression engines, the overall throughput will be N x 300MB/s. For example, if you have 8 compression engines, then the overall throuput will be 8 x 300 = 2.4GB/s.
Note
This is a generic architecture to cover all the LZ based algorithms (LZ77, LZ4, LZO and Snappy).
Compression Kernel Design¶
The design for LZ compression kernel is shown in the following figure:
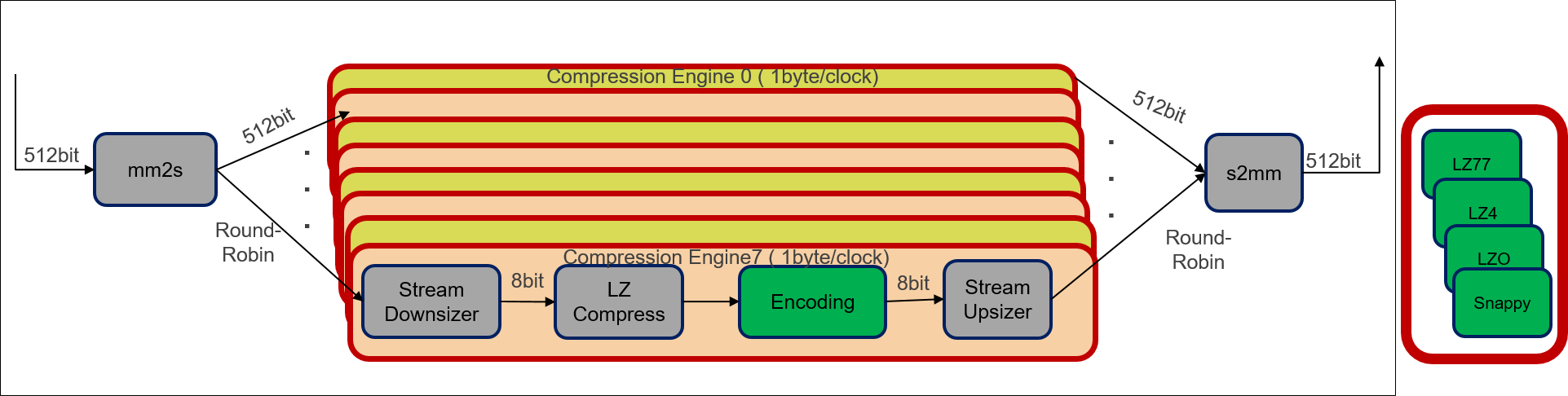
The following is a description of the LZ based compression kernel design process:
- Input data is divided into muliple blocks with 64K default block size (user configurable). Each block is sent to an individual compression engine to compress concurrently in a round-robin fashion.
- Input unit(mm2s block) reads the uncompressed blocks from the global memory(512 bit wide) and distributes them across multiple parallel compression engines. Output unit(s2mm block) reads compressed block from the compression engines and writes to the global memory.
- Each Compression engine contains a series of sub-modules, which process data parallelly and work in a pipelined fashion. Each sub-module transfers data to the next module using the HLS streams. Each sub-module is designed to process 1 byte/clock cycle, which along with pipelined processing, makes the throughput of each compression a 1 byte/clock cycle.
- Data read from the global memory is converted to a byte stream by the mm2s block and back to memory mapped from stream by the s2mm block for writing to the global memory.
The compression engine design remains same for all LZ based compression algorithms. Only difference is the Encoding sub-module in compression engine module, which is unique for each algorithm.
Decompression Kernel Design¶
The design for LZ decompression kernel is shown in the following figure:
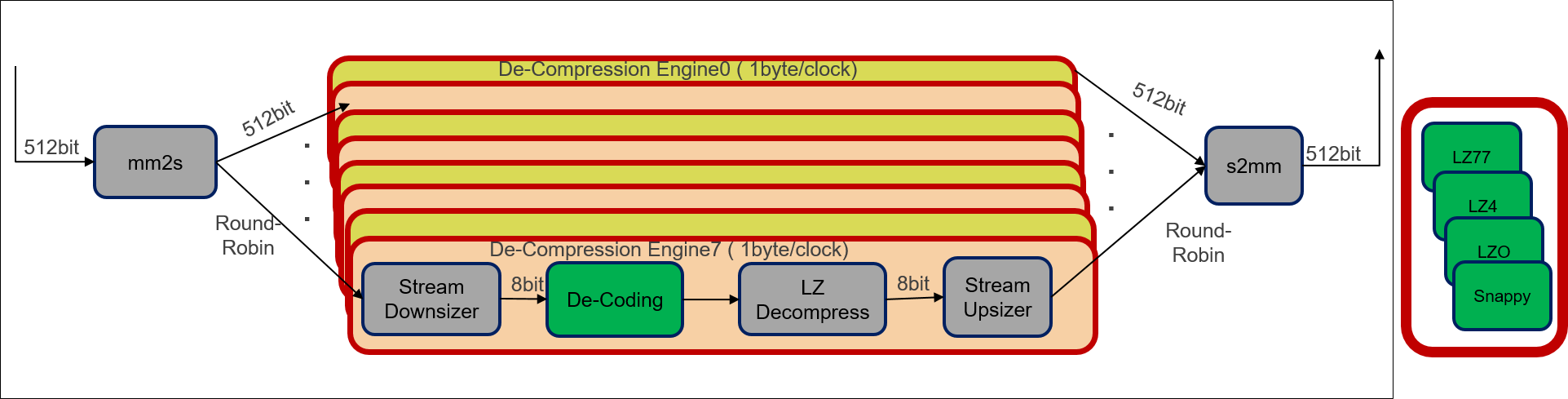
The following is a description of the LZ based decompression kernel design process:
- The overall design remains similar to the compression kernel design. Input data is read from the global memory, converted to stream and distributed across the decompression engines in a round robin fashion.
- Each decompression engine module contains multiple sub-modules processing 1 byte per clock cycle. The modules work in a pipelined fashion, therefore, the throughput of each decompression engine is 1 byte per clock cycle.
The decompression engine design also remains same for all LZ based algorithms. The only difference is the Decoding sub-module in decompression engine module, which is unique for each algorithm.
Implemented Algorithms¶
The following is a list of implemented compression algorithms: