Internal Design of Markov Chain Monte Carlo¶
Overview¶
The Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is a computer-driven sampling method. It allows one to characterize a distribution without knowing all of the distribution’s mathematical properties by randomly sampling values out of the distribution. A particular strength of MCMC is that it can be used to draw samples from distributions even when all that is known about the distribution is how to calculate the density for different samples. This implementation is Population MCMC using Parallel Tempering. Multi-chain implementation allows to generate samples from multi-mode distribution
The Engine (pop_mcmc.h)¶
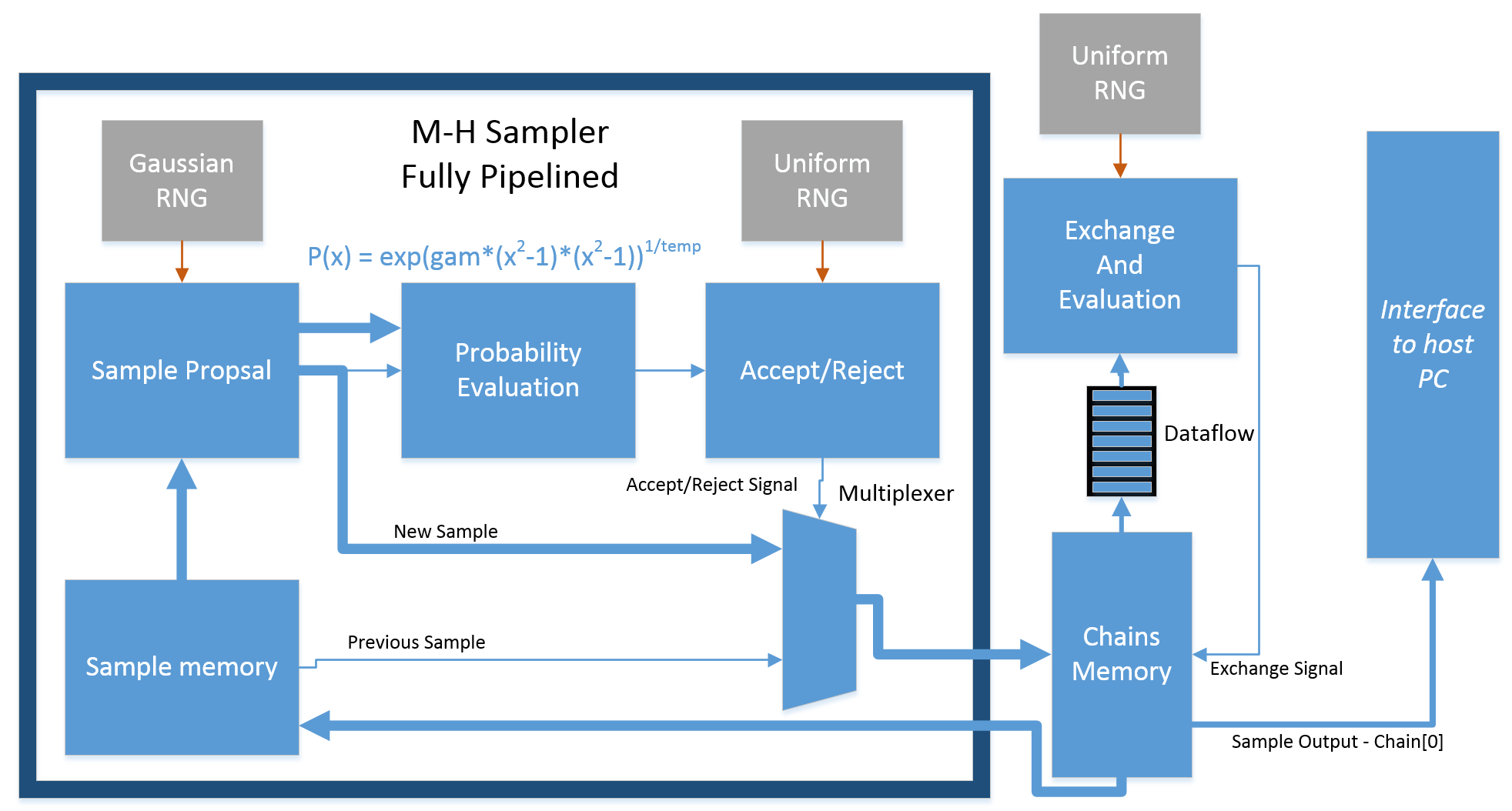
The engine is templated to generate either a floating point (Float-32) samples or a double (Float-64) samples. Target distribution function is part of the engine. The Metropolis-Hastings algorithm is used for sampling. Proposal is generated from Normal distribution using Inverse Cumulative Distributed Function based and Box-Muller transformation (MT19937IcnRng). There are 3 Random number generators in total working in parallel (One NRNG for proposal and two Uniform RNGs for acceptance function). The engine is split into two main processes : Chain sample and Chain exchange working in Dataflow region, both fully pipelined for chains. There were many additional optimizations applied for high performance. Part of proposal generation for next sample is running in parallel with current sample generation. For memory optimization, only one sample is stored for each chain.
The following is the architecture of the engine: