Row-wise Accumulator Implementation¶
This page provides the Row-wise accumulator implementation details. The following figure shows the row-wise accumulator logic:
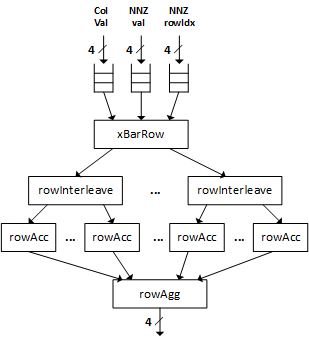
- There are three input streams, namely the columnvector value stream, the NNZ value stream and the NNZ row indices stream.
- Each stream contains multiple entries being processed in parallel. For example, the
4entries shown in the figure. - The number of parallel entries can be configured at the compile time by
SPARSE_parEntries. - The
xBarRowlogic carries out the multiplication of the column value and the NNZ value, and distributes the results and their corresponding row indices to the accumulator logic implemented by therowInterleaveandrowAccmodules. - The
`rowInterleavemodule is designed to address the long latency of floating point accumulation by overprovising the accumulators. - Each
rowInterleavemodule will drive severalrowAccmodules for row-wise accumulation. The number ofrowInterleavemodules is configured at compile time bySPARSE_parEntries. - The number of
rowAccmodules driven by eachrowInterleavemodule is configured bySPARSE_parGroupsat the compile time. - There is a on-chip memory block in each
rowAccmodule to store the accumulation results. - Once the accumulation operation is finished, each
rowAccmodule will read out the data in the on-chip memory and send them torowAggmodule to be merged together and written to the device memory, for example, HBM.