XRT Native Library C++ API¶
Buffer APIs¶
-
class xrt::bo¶
Public Types
-
enum class flags : uint32_t¶
buffer object flags
Values:
-
enumerator normal¶
Create normal BO with host side and device side buffers
-
enumerator cacheable¶
Create cacheable BO. Only effective on embedded platforms.
-
enumerator device_only¶
Create a BO with a device side buffer only
-
enumerator host_only¶
Create a BO with a host side buffer only
-
enumerator p2p¶
Create a BO for peer-to-peer use
Public Functions
-
bo(const xrt::device &device, void *userptr, size_t sz, bo::flags flags, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor with user host buffer and flags
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
device – The device on which to allocate this buffer
userptr – Pointer to aligned user memory
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::device &device, void *userptr, size_t sz, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor with user host buffer and default flags
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
device – The device on which to allocate this buffer
userptr – Pointer to aligned user memory
sz – Size of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::device &device, size_t sz, bo::flags flags, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor where XRT manages host buffer if needed
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
device – The device on which to allocate this buffer
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::device &device, size_t sz, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor, default flags, where XRT manages host buffer if any
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
device – The device on which to allocate this buffer
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::hw_context &hwctx, void *userptr, size_t sz, bo::flags flags, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor with user host buffer and flags
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
hwctx – The hardware context in which to allocate this buffer
userptr – Pointer to aligned user memory
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::hw_context &hwctx, void *userptr, size_t sz, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor with user host buffer and default flags
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
hwctx – The hardware context in which to allocate this buffer
userptr – Pointer to aligned user memory
sz – Size of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::hw_context &hwctx, size_t sz, bo::flags flags, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor where XRT manages host buffer if needed
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
hwctx – The hardware context in which to allocate this buffer
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(const xrt::hw_context &hwctx, size_t sz, memory_group grp)¶
bo() - Constructor, default flags, where XRT manages host buffer if any
The device memory group depends on connectivity. If the buffer as a kernel argument, then the memory group can be obtained from the xrt::kernel object.
- Parameters
hwctx – The hardware context in which to allocate this buffer
sz – Size of buffer
flags – Specify type of buffer
grp – Device memory group to allocate buffer in
-
bo(xclDeviceHandle dhdl, xclBufferExportHandle ehdl)¶
bo() - Constructor to import an exported buffer
If the exported buffer handle acquired by using the export() method is from another process, then it must be transferred through proper IPC mechanism translating the underlying file-descriptor asscociated with the buffer, see also constructor taking process id as argument.
- Parameters
dhdl – Device that imports the exported buffer
ehdl – Exported buffer handle, implementation specific type
-
bo(xclDeviceHandle dhdl, pid_type pid, xclBufferExportHandle ehdl)¶
bo() - Constructor to import an exported buffer from another process
The exported buffer handle is obtained from exporting process by calling
export(). This contructor requires that XRT is built on and running on a system with pidfd support. Also the importing process must have permission to duplicate the exporting process’ file descriptor. This permission is controlled by ptrace access mode PTRACE_MODE_ATTACH_REALCREDS check (see ptrace(2)).- Parameters
dhdl – Device that imports the exported buffer
pid – Process id of exporting process
ehdl – Exported buffer handle, implementation specific type
-
bo(const bo &parent, size_t size, size_t offset)¶
bo() - Constructor for sub-buffer
- Parameters
parent – Parent buffer
size – Size of sub-buffer
offset – Offset into parent buffer
-
inline explicit operator bool() const¶
operator bool() - Check if bo handle is valid
-
uint64_t address() const¶
address() - Get the device address of this buffer
- Returns
Device address of buffer
-
memory_group get_memory_group() const¶
get_memory_group() - Get the memory group in which this buffer is allocated
- Returns
Memory group index with which the buffer was constructed
-
flags get_flags() const¶
get_flags() - Get the flags with which this buffer was constructed
- Returns
The xrt::bo::Flgas used when the buffer was contructed
-
xclBufferExportHandle export_buffer()¶
buffer_export() - Export this buffer
An exported buffer can be imported on another device by this process or another process. For multiprocess transfer, the exported buffer must be transferred through a proper IPC facility to translate the underlying file-descriptor properly into another process.
The lifetime of the exported buffer handle is associated with the exporting buffer (this). The handle is disposed of when the exporting buffer is destructed.
It is undefined behavior to use the export handle after the exporting buffer object has gone out of scope.
- Returns
Exported buffer handle
-
async_handle async(xclBOSyncDirection dir, size_t sz, size_t offset)¶
async() - Start buffer content txfer with device side
Asynchronously transfer specified size bytes of buffer starting at specified offset.
- Parameters
dir – To device or from device
sz – Size of data to synchronize
offset – Offset within the BO
-
inline async_handle async(xclBOSyncDirection dir)¶
async() - Start buffer content txfer with device side
Asynchronously transfer entire buffer content in specified direction
- Parameters
dir – To device or from device
sz – Size of data to synchronize
offset – Offset within the BO
-
void sync(xclBOSyncDirection dir, size_t sz, size_t offset)¶
sync() - Synchronize buffer content with device side
Sync specified size bytes of buffer starting at specified offset.
- Parameters
dir – To device or from device
sz – Size of data to synchronize
offset – Offset within the BO
-
inline void sync(xclBOSyncDirection dir)¶
sync() - Synchronize buffer content with device side
Sync entire buffer content in specified direction.
- Parameters
dir – To device or from device
-
void *map()¶
map() - Map the host side buffer into application
Map the contents of the buffer object into host memory
- Returns
Memory mapped buffer
-
template<typename MapType>
inline MapType map()¶ map() - Map the host side buffer info application
- Template Parameters
MapType – Type of mapped data
- Returns
Memory mapped buffer
-
void write(const void *src, size_t size, size_t seek)¶
write() - Copy-in user data to host backing storage of BO
Copy source data to host buffer of this buffer object.
seekspecifies how many bytes to skip at the beginning of the BO before copying-insizebytes to host buffer.If BO has no host backing storage, e.g. a device only buffer, then write is directly to the device buffer.
- Parameters
src – Source data pointer
size – Size of data to copy
seek – Offset within the BO
-
inline void write(const void *src)¶
write() - Copy-in user data to host backing storage of BO
Copy specified source data to host buffer of this buffer object.
If BO has no host backing storage, e.g. a device only buffer, then write is directly to the device buffer.
- Parameters
src – Source data pointer
-
void read(void *dst, size_t size, size_t skip)¶
read() - Copy-out user data from host backing storage of BO
Copy content of host buffer of this buffer object to specified destination.
skipspecifies how many bytes to skip from the beginning of the BO before copying-outsizebytes of host buffer.If BO has no host backing storage, e.g. a device only buffer, then read is directly from the device buffer.
- Parameters
dst – Destination data pointer
size – Size of data to copy
skip – Offset within the BO
-
inline void read(void *dst)¶
read() - Copy-out user data from host backing storage of BO
Copy content of host buffer of this buffer object to specified destination.
If BO has no host backing storage, e.g. a device only buffer, then read is directly from the device buffer.
- Parameters
dst – Destination data pointer
-
void copy(const bo &src, size_t sz, size_t src_offset = 0, size_t dst_offset = 0)¶
copy() - Deep copy BO content from another buffer
Throws if copy size is 0 or sz + src/dst_offset is out of bounds.
- Parameters
src – Source BO to copy from
sz – Size of data to copy
src_offset – Offset into src buffer copy from
dst_offset – Offset into this buffer to copy to
-
class async_handle : public detail::pimpl<async_handle_impl>¶
xrt::bo::async_handle represents an asynchronously operation
A handle object is returned from asynchronous buffer object operations. It can be used to wait for the operation to complete.
-
enum class flags : uint32_t¶
Configuration APIs¶
-
namespace xrt::ini¶
APIs for XRT configuration control.
XRT can be configured through a json xrt.ini file co-located with the host executable. If present, XRT uses configuration options from the ini file when a given option is first accessed. Without an ini file, the configuration options take on default values.
The APIs in this file allow host application to specify configuration options for XRT programatically. It is only possible for the host application to change configuration options before a given option is used by XRT the very first time.
Custom IP APIs¶
-
class xrt::ip : public detail::pimpl<ip_impl>¶
xrt::ip represent the custom IP
The ip can be controlled through read- and write register only. If the IP supports interrupt notification, then xrt::ip objects supports enabling and control of underlying IP interrupt.
In order to construct an ip object, the following requirements must be met:
The custom IP must appear in IP_LAYOUT section of xclbin.
The custom IP must have a base address such that it can be controlled through register access at offsets from base address.
The custom IP must have an address range so that write and read access to base address offset can be validated.
XRT supports exclusive access only for the custom IP, this is to other processes from accessing the same IP at the same time.
Public Functions
-
ip(const xrt::device &device, const xrt::uuid &xclbin_id, const std::string &name)¶
ip() - Constructor from a device and xclbin
The IP is opened with exclusive access meaning that no other xrt::ip objects can use the same IP, nor will another process be able to use the IP while one process has been granted access.
Constructor throws on error.
- Parameters
device – Device programmed with the IP
xclbin_id – UUID of the xclbin with the IP
name – Name of IP to construct
-
void write_register(uint32_t offset, uint32_t data)¶
write_register() - Write to the address range of an ip
Throws std::out_or_range if offset is outside the ip address space
- Parameters
offset – Offset in register space to write to
data – Data to write
-
uint32_t read_register(uint32_t offset) const¶
read_register() - Read data from ip address range
Throws std::out_or_range if offset is outside the ip address space
- Parameters
offset – Offset in register space to read from
- Returns
Value read from offset
-
interrupt create_interrupt_notify()¶
create_interrupt_notify() - Create xrt::ip::interrupt object
This function creates an xrt::ip::interrupt object that can be used to control and wait for IP interrupt. On successful return the IP has interrupt enabled.
Throws if the custom IP doesn’t support interrupts.
- Returns
xrt::ip::interrupt object can be used to control IP interrupt.
-
class interrupt : public detail::pimpl<interrupt_impl>¶
xrt::ip::interrupt represents an IP interrupt event.
This class represents an IP interrupt event. The interrupt object is contructed via
xrt::ip::create_interrupt_notify(). The object can be used to enable and disable IP interrupts and to wait for an interrupt to occur.Upon construction, the IP interrupt is automatically enabled.
Public Functions
-
void enable()¶
enable() - Enable interrupt
Enables the IP interrupt if not already enabled. The IP interrupt is automatically enabled when the interrupt object is created.
-
void wait()¶
wait() - Wait for interrupt
Wait for interrupt from IP. Upon return, interrupt is re-enabled.
-
std::cv_status wait(const std::chrono::milliseconds &timeout) const¶
wait() - Wait for interrupt or timeout to occur
Blocks the current thread until an interrupt is received from the IP, or until after the specified timeout duration
- Parameters
timeout – Timout in milliseconds.
- Returns
std::cv_status::timeout if the timeout specified expired, std::cv_status::no_timeout otherwise.
-
void enable()¶
Device APIs¶
-
class xrt::device¶
xrt::device represents used for acceleration.
Public Functions
-
explicit device(unsigned int didx)¶
device() - Constructor from device index
Throws if no device is found matching the specified index.
- Parameters
didx – Device index
-
explicit device(const std::string &bdf)¶
device() - Constructor from string
If the string is in BDF format it matched against devices installed on the system. Otherwise the string is assumed to be a device index.
Throws if string format is invalid or no matching device is found.
- Parameters
bdf – String identifying the device to open.
-
explicit device(xclDeviceHandle dhdl)¶
device() - Create a managed device object from a shim xclDeviceHandle
- Parameters
dhdl – Shim xclDeviceHandle
- Returns
xrt::device object epresenting the opened device, or exception on error
-
template<info::device param>
inline info::param_traits<info::device, param>::return_type get_info() const¶ get_info() - Retrieve device parameter information
This function is templated on the enumeration value as defined in the enumeration xrt::info::device.
The return type of the parameter is based on the instantiated param_traits for the given param enumeration supplied as template argument, see namespace xrt::info
This function guarantees return values conforming to the format used by the time the application was built and for a two year period minimum. In other words, XRT can be updated to new versions without affecting the format of the return type.
-
uuid load_xclbin(const axlf *xclbin)¶
load_xclbin() - Load an xclbin
- Parameters
xclbin – Pointer to xclbin in memory image
- Returns
UUID of argument xclbin
-
uuid load_xclbin(const std::string &xclbin_fnm)¶
load_xclbin() - Read and load an xclbin file
This function reads the file from disk and loads the xclbin. Using this function allows one time allocation of data that needs to be kept in memory.
- Parameters
xclbin_fnm – Full path to xclbin file
- Returns
UUID of argument xclbin
-
uuid load_xclbin(const xrt::xclbin &xclbin)¶
load_xclbin() - load an xclin from an xclbin object
This function uses the specified xrt::xclbin object created by caller. The xrt::xclbin object must contain the complete axlf structure.
- Parameters
xclbin – xrt::xclbin object
- Returns
UUID of argument xclbin
-
uuid get_xclbin_uuid() const¶
get_xclbin_uuid() - Get UUID of xclbin image loaded on device
Note that current UUID can be different from the UUID of the xclbin loaded by this process using load_xclbin()
- Returns
UUID of currently loaded xclbin
-
template<typename SectionType>
inline SectionType get_xclbin_section(axlf_section_kind section, const uuid &uuid) const¶ get_xclbin_section() - Retrieve specified xclbin section
Get the xclbin section of the xclbin currently loaded on the device. The function throws on error
Note, this API may be replaced with more generic query request access
- Parameters
section – The section to retrieve
uuid – Xclbin uuid of the xclbin with the section to retrieve
- Returns
The specified section if available.
-
explicit device(unsigned int didx)¶
Info APIs¶
-
namespace xrt::info¶
Enums
-
enum class device : unsigned int¶
Device information parameters.
Use with
xrt::device::get_info()to retrieve properties of the device. The type of the device properties is compile time defined with param traits.Values:
-
enumerator bdf¶
BDF for device (std::string)
-
enumerator kdma¶
Number of KDMA engines (std::uint32_t)
-
enumerator max_clock_frequency_mhz¶
Max clock frequency (unsigned long)
-
enumerator m2m¶
True if device contains m2m (bool)
-
enumerator name¶
Name (VBNV) of device (std::string)
-
enumerator nodma¶
True if device is a NoDMA device (bool)
-
enumerator offline¶
True if device is offline and in process of being reset (bool)
-
enumerator electrical¶
Electrical and power sensors present on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator thermal¶
Thermal sensors present on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator mechanical¶
Mechanical sensors on and surrounding the device (std::string)
-
enumerator memory¶
Memory information present on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator platform¶
Platforms flashed on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator pcie_info¶
Pcie information of the device (std::string)
-
enumerator host¶
Host information (std::string)
-
enumerator aie¶
AIE core information of the device (std::string)
-
enumerator aie_shim¶
AIE shim information of the device (std::string)
-
enumerator dynamic_regions¶
Information about xclbin on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator vmr¶
Information about vmr on the device (std::string)
-
enumerator aie_mem¶
AIE memory information of the device (std::string)
-
enumerator bdf¶
-
enum class device : unsigned int¶
Kernel APIs¶
-
class xrt::kernel¶
A kernel object represents a set of instances matching a specified name. The kernel is created by finding matching kernel instances in the currently loaded xclbin.
Most interaction with kernel objects are through xrt::run objects created from the kernel object to represent an execution of the kernel
Public Functions
-
kernel(const xrt::device &device, const xrt::uuid &xclbin_id, const std::string &name, cu_access_mode mode = cu_access_mode::shared)¶
kernel() - Constructor from a device and xclbin
The kernel name must uniquely identify compatible kernel instances (compute units). Optionally specify which kernel instance(s) to open using “kernelname:{instancename1,instancename2,…}” syntax. The compute units are default opened with shared access, meaning that other kernels and other process will have shared access to same compute units.
- Parameters
device – Device on which the kernel should execute
xclbin_id – UUID of the xclbin with the kernel
name – Name of kernel to construct
mode – Open the kernel instances with specified access (default shared)
-
template<typename ...Args>
inline run operator()(Args&&... args)¶ operator() - Invoke the kernel function
- Parameters
args – Kernel arguments
- Returns
Run object representing this kernel function invocation
-
int group_id(int argno) const¶
group_id() - Get the memory bank group id of an kernel argument
The function throws if the group id is ambigious.
- Parameters
argno – The argument index
- Returns
The memory group id to use when allocating buffers (see xrt::bo)
-
uint32_t offset(int argno) const¶
offset() - Get the offset of kernel argument
Use with
read_register()andwrite_register()if manually reading or writing kernel registers for explicit arguments.- Parameters
argno – The argument index
- Returns
The kernel register offset of the argument with specified index
-
std::string get_name() const¶
get_name() - Return the name of the kernel
-
xrt::xclbin get_xclbin() const¶
get_xclbin() - Return the xclbin containing the kernel
-
kernel(const xrt::device &device, const xrt::uuid &xclbin_id, const std::string &name, cu_access_mode mode = cu_access_mode::shared)¶
-
class xrt::run¶
xrt::run represents one execution of a kernel
The run handle can be explicitly constructed from a kernel object or implicitly constructed from starting a kernel execution.
A run handle can be re-used to execute the same kernel again.
Public Functions
-
explicit run(const kernel &krnl)¶
run() - Construct run object from a kernel object
- Parameters
krnl – Kernel object representing the kernel to execute
-
void start()¶
start() - Start one execution of a run.
This function is asynchronous, run status must be expclicit checked or
wait()must be used to wait for the run to complete.
-
void start(const autostart &iterations)¶
start() - Start auto-restart execution of a run
An iteration count of zero means that the kernel should run forever, or until explicitly stopped using
stop().This function is asynchronous, run status must be expclicit checked or
wait()must be used to wait for the run to complete.The kernel run object is complete only after all iterations have completed, or until run object has been explicitly stopped.
Changing kernel arguments
set_arg()while the kernel is running has undefined behavior. To synchronize change of arguments, please use xrt::mailbox.Currently autostart is only supported for kernels with one compute unit which must be opened in exclusive mode.
- Parameters
iterations – Number of times to iterate the same run.
-
void stop()¶
stop() - Stop kernel run object at next safe iteration
If the kernel run object has been started by specifying an iteration count or by specifying default iteration count, then this function can be used to stop the iteration early.
The function is synchronous and waits for the kernel run object to complete.
If the kernel is not iterating, then calling this funciton is the same as calling
wait().
-
ert_cmd_state abort()¶
abort() - Abort a run object that has been started
If the run object has been sent to scheduler for execution, then this function can be used to abort the scheduled command.
The function is synchronous and will wait for abort to complete. The return value is the state of the aborted command.
- Returns
State of aborted command
-
ert_cmd_state wait(const std::chrono::milliseconds &timeout = std::chrono::milliseconds{0}) const¶
wait() - Wait for a run to complete execution
The default timeout of 0ms indicates blocking until run completes.
The current thread will block until the run completes or timeout expires. Completion does not guarantee success, the run status should be checked by using
state.If specified time out is exceeded, the function returns with ERT_CMD_STATE_TIMEOUT, it is the callers responsibility to abort the run if it continues to time out.
The current implementation of this API can mask out the timeout of this run so that the call either never returns or doesn’t return until the run completes by itself. This can happen if other runs are continuosly completing within the specified timeout for this run. If the device is otherwise idle, or if the time between run completion exceeds the specified timeout, then this function will identify the timeout.
- Parameters
timeout – Timeout for wait (default block till run completes)
- Returns
Command state upon return of wait, or ERT_CMD_STATE_TIMEOUT if timeout exceeded.
-
inline ert_cmd_state wait(unsigned int timeout_ms) const¶
wait() - Wait for specified milliseconds for run to complete
The default timeout of 0ms indicates blocking until run completes.
The current thread will block until the run completes or timeout expires. Completion does not guarantee success, the run status should be checked by using
state.If specified time out is exceeded, the function returns with ERT_CMD_STATE_TIMEOUT, it is the callers responsibility to abort the run if it continues to time out.
The current implementation of this API can mask out the timeout of this run so that the call either never returns or doesn’t return until the run completes by itself. This can happen if other runs are continuosly completing within the specified timeout for this run. If the device is otherwise idle, or if the time between run completion exceeds the specified timeout, then this function will identify the timeout.
- Parameters
timeout_ms – Timeout in milliseconds
- Returns
Command state upon return of wait, or ERT_CMD_STATE_TIMEOUT if timeout exceeded.
-
std::cv_status wait2(const std::chrono::milliseconds &timeout) const¶
wait2() - Wait for specified milliseconds for run to complete
Successful command completion means that the command state is ERT_CMD_STATE_COMPLETED. All other command states result in this function throwing
command_errorexception with the command state embedded in the exception.Throws
xrt::run::command_erroron abnormal command termination.The current thread blocks until the run successfully completes or timeout expires. A return code of std::cv_state::no_timeout guarantees that the command completed successfully.
If specified time out is exceeded, the function returns with std::cv_status::timeout, it is the callers responsibility to abort the run if it continues to time out.
The current implementation of this API can mask out the timeout of this run so that the call either never returns or doesn’t return until the run completes by itself. This can happen if other runs are continuosly completing within the specified timeout for this run. If the device is otherwise idle, or if the time between run completion exceeds the specified timeout, then this function will identify the timeout.
- Parameters
timeout – Timeout for wait (default block until run completes)
- Returns
std::cv_status::no_timeout when command completes successfully. std::cv_status::timeout when wait timed out without command completing.
-
inline void wait2() const¶
wait2() - Wait for successful command completion
Successful command completion means that the command state is ERT_CMD_STATE_COMPLETED. All other command states result in this function throwing
command_errorexception with the command state embedded in the exception.Throws
xrt::run::command_erroron abnormal command termination.
-
ert_cmd_state state() const¶
state() - Check the current state of a run object
The state values are defined in
include/ert.h- Returns
Current state of this run object
-
uint32_t return_code() const¶
return_code() - Get the return code from PS kernel
- Returns
Return code from PS kernel run
-
void add_callback(ert_cmd_state state, std::function<void(const void*, ert_cmd_state, void*)> callback, void *data)¶
add_callback() - Add a callback function for run state
The function is called when the run object changes state to argument state or any error state. Only
ERT_CMD_STATE_COMPLETEDis supported currently.The function object’s first parameter is a unique ‘key’ for this xrt::run object implmentation on which the callback was added. This ‘key’ can be used to identify an actual run object that refers to the implementaion that is maybe shared by multiple xrt::run objects.
Any number of callbacks are supported.
- Parameters
state – State to invoke callback on
callback – Callback function
data – User data to pass to callback function
-
inline explicit operator bool() const¶
operator bool() - Check if run handle is valid
- Returns
True if run is associated with kernel object, false otherwise
-
inline bool operator<(const xrt::run &rhs) const¶
operator < () - Weak ordering
- Parameters
rhs – Object to compare with
- Returns
True if object is ordered less that compared with other
-
template<typename ArgType>
inline void set_arg(int index, ArgType &&arg)¶ set_arg() - Set a specific kernel scalar argument for this run
Use this API to explicit set or change a kernel argument prior to starting kernel execution. After setting arguments, the kernel can be started using
start()on the run object.See also
operator()to set all arguments and start kernel.- Parameters
index – Index of kernel argument to update
arg – The scalar argument value to set.
-
inline void set_arg(int index, xrt::bo &boh)¶
set_arg() - Set a specific kernel global argument for a run
Use this API to explicit set or change a kernel argument prior to starting kernel execution. After setting arguments, the kernel can be started using
start()on the run object.See also
operator()to set all arguments and start kernel.- Parameters
index – Index of kernel argument to set
boh – The global buffer argument value to set (lvalue).
-
template<typename ArgType>
inline void set_arg(const std::string &argnm, ArgType &&argvalue)¶ set_arg - set named argument
Throws if specified argument name doesn’t match kernel specification. Throws if argument value is incompatible with specified argument
- Parameters
argnm – Name of kernel argument
argvalue – Argument value
-
template<typename ArgType>
inline void update_arg(int index, ArgType &&arg)¶ udpdate_arg() - Asynchronous update of scalar kernel global argument
Use this API to asynchronously update a specific scalar argument of the kernel associated with the run object.
This API is only supported on Edge.
- Parameters
index – Index of kernel argument to update
arg – The scalar argument value to set.
-
inline void update_arg(int index, const xrt::bo &boh)¶
update_arg() - Asynchronous update of kernel global argument for a run
Use this API to asynchronously update a specific kernel argument of an existing run.
This API is only supported on Edge.
- Parameters
index – Index of kernel argument to update
boh – The global buffer argument value to set.
-
template<typename ...Args>
inline void operator()(Args&&... args)¶ operator() - Set all kernel arguments and start the run
Use this API to explicitly set all kernel arguments and start kernel execution.
- Parameters
args – Kernel arguments
-
template<typename ...Args>
inline void operator()(autostart &&count, Args&&... args)¶ operator() - Set all kernel arguments and start the run
Use this API to explicitly set all kernel arguments and start kernel execution for specified number of iterations.
An iteration count of ‘1’ invokes the kernel once and is the same as calling the operator without specifying
autostart.The run is complete only after all iterations have completed or when the kernel has been explicitly stopped using
stop().Currently autostart is only supported for kernels with one compute unit which must be opened in exclusive mode.
- Parameters
count – Iteration count specifying number of iterations of the run
args – Kernel arguments
-
class command_error : public detail::pimpl<command_error_impl>, public std::exception¶
Public Functions
-
ert_cmd_state get_command_state() const¶
get_command_state() - command state upon completion
-
ert_cmd_state get_command_state() const¶
-
explicit run(const kernel &krnl)¶
Message APIs¶
-
namespace xrt::message¶
APIs for XRT messaging.
XRT internally uses a message system that supports dispatching of messages to null, console, file, or syslog under different verbosity levels. The sink and verbosity level is controlled statically through
xrt.inior at run-time usingxrt::ini.The APIs in this file allow host application to use the same message dispatch mechanism as XRT is configured to use.
Enums
-
enum class level : unsigned short¶
Verbosity level for messages.
Use logging APIs to control at what verbosity level the messages should be issued. The default verbosity can be changed in
xrt.inior programatically by usingxrt::ini::set.Values:
-
enumerator emergency¶
-
enumerator alert¶
-
enumerator critical¶
-
enumerator error¶
-
enumerator warning¶
-
enumerator notice¶
-
enumerator info¶
-
enumerator debug¶
-
enumerator emergency¶
Functions
-
void log(level lvl, const std::string &tag, const std::string &msg)¶
log() - Dispatch composed log message
- Parameters
lvl – Severity level, the message is ignored if configured level is less than specified level.
tag – The message tag to use.
msg – A formatted composed message
-
template<typename ...Args>
void logf(level lvl, const std::string &tag, const char *format, Args&&... args)¶ logf() - Compose and dispatch formatted log message
This log function uses boost::format to compose the message from specified format string and arguments.
- Parameters
lvl – Severity level, the message is ignored if configured level is less than specified level.
tag – The message tag to use.
format – A format string similar to printf or boost::format
args – Message arguments for the placeholders used in the format string
-
enum class level : unsigned short¶
System APIs¶
-
namespace xrt::system¶
APIs for system level queries and control.
Functions
-
unsigned int enumerate_devices()¶
enumerate_devices() - Enumerate devices found in the system
- Returns
Number of devices in the system recognized by XRT
-
unsigned int enumerate_devices()¶
UUID APIs¶
-
class xrt::uuid¶
Wrapper class to treat uuid_t as a value type supporting copying.
xrt::uuid is used by many XRT APIs to match an expected xclbin against current device xclbin, or to get the uuid of current loaded shell on the device.
Public Functions
-
inline uuid(const xuid_t val)¶
uuid() - Construct uuid from a basic bare uuid
A basic uuid is either a uuid_t on Linux, or a typedef of equivalent basic type of other platforms
- Parameters
val – The basic uuid to construct this object from
-
inline explicit uuid(const std::string &uuid_str)¶
uuid() - Construct uuid from a string representaition
A uuid string is 36 bytes with ‘-’ at 8, 13, 18, and 23
- Parameters
uuid_str – A string formatted as a uuid string
-
inline uuid &operator=(const uuid &rhs)¶
operator=() - assignment
- Parameters
rhs – Value to be assigned from
- Returns
Reference to this
-
inline const xuid_t &get() const¶
get() - Get the underlying basis uuid type value
A basic uuid is either a uuid_t on Linux, or a typedef of equivalent basic type of other platforms
- Returns
Basic uuid value
-
inline std::string to_string() const¶
to_string() - Convert to string
- Returns
Lower case string representation of this uuid
-
inline operator bool() const¶
bool() - Conversion operator
- Returns
True if this uuid is not null
-
inline bool operator==(const xuid_t &xuid) const¶
operator==() - Compare to basic uuid
A basic uuid is either a uuid_t on Linux, or a typedef of equivalent basic type of other platforms
- Parameters
xuid – Basic uuid to compare against
- Returns
True if equal, false otherwise
-
inline bool operator!=(const xuid_t &xuid) const¶
operator!=() - Compare to basic uuid
A basic uuid is either a uuid_t on Linux, or a typedef of equivalent basic type of other platforms
- Parameters
xuid – Basic uuid to compare against
- Returns
False if equal, true otherwise
-
inline bool operator==(const uuid &rhs) const¶
operator==() - Comparison
- Parameters
rhs – uuid to compare against
- Returns
True if equal, false otherwise
-
inline bool operator!=(const uuid &rhs) const¶
operator!=() - Comparison
- Parameters
rhs – uuid to compare against
- Returns
False if equal, true otherwise
-
inline bool operator<(const uuid &rhs) const¶
operator<() - Comparison
- Parameters
rhs – uuid to compare against
- Returns
True of this is less that argument uuid, false otherwise
-
inline uuid(const xuid_t val)¶
XCLBIN APIs¶
-
class xrt::xclbin : public detail::pimpl<xclbin_impl>¶
xrt::xclbin represents an xclbin and provides APIs to access meta data.
The xclbin object is constructed by the user from a file.
When the xclbin object is constructed from a complete xclbin, then it can be used by xrt::device to program the xclbin onto the device.
First-class objects and class navigation
All meta data is rooted at xrt::xclbin.
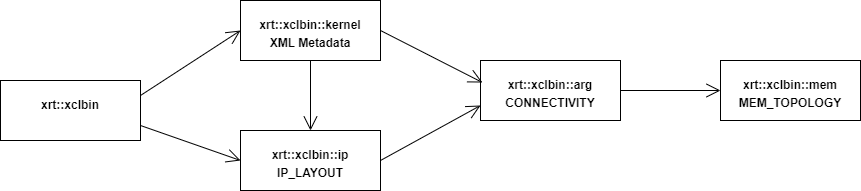
From the xclbin object xrt::xclbin::kernel or xrt::xclbin::ip objects can be constructed.
The xrt:xclbin::kernel is a concept modelled only in the xclbin XML metadata, it corresponds to a function that can be executed by one or more compute units modelled by xrt::xclbin::ip objects. An xrt::xclbin::ip object corresponds to an entry in the xclbin IP_LAYOUT section, so the xrt::xclbin::kernel object is just a grouping of one or more of these.
In some cases the kernel concept is not needed, thus xrt::xclbin::ip objects corresponding to entries in the xclbin IP_LAYOUT sections can be accessed directly.
An xrt::xclbin::arg object corresponds to one or more entries in the xclbin CONNECTIVITY section decorated with additional meta data (offset, size, type, etc) from the XML section if available. An argument object represents a specific kernel or ip argument. If the argument is a global buffer, then it may connect to one or more memory objects.
Finally the xrt::xclbin::mem object corresponds to an entry in the MEM_TOPOLOGY section of the xclbin.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
explicit xclbin(const std::string &filename)¶
xclbin() - Constructor from an xclbin filename
Throws if file not found.
- Parameters
filename – Path to the xclbin file
-
explicit xclbin(const std::vector<char> &data)¶
xclbin() - Constructor from raw data
The raw data of the xclbin can be deleted after calling the constructor.
- Parameters
data – Raw data of xclbin
-
explicit xclbin(const axlf *top)¶
xclbin() - Constructor from raw data
The argument axlf is copied by the constructor.
- Parameters
top – Raw data of xclbin file as axlf*
-
std::vector<kernel> get_kernels() const¶
get_kernels() - Get list of kernels from xclbin.
Kernels are extracted from embedded XML metadata in the xclbin. A kernel groups one or more compute units. A kernel has arguments from which offset, type, etc can be retrived.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::kernel from xclbin.
-
kernel get_kernel(const std::string &name) const¶
get_kernel() - Get a kernel by name from xclbin
A matching kernel is extracted from embedded XML metadata in the xclbin. A kernel groups one or more compute units. A kernel has arguments from which offset, type, etc can be retrived.
- Parameters
name – Name of kernel to get.
- Returns
The matching kernel from the xclbin or error if no matching kernel is found.
-
std::vector<ip> get_ips() const¶
get_ips() - Get a list of IPs from the xclbin
The returned xrt::xclbin::ip objects are extracted from the IP_LAYOUT section of the xclbin.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::ip objects from xclbin.
-
std::vector<ip> get_ips(const std::string &name) const¶
get_ips() - Get list of ips that matches name
The kernel name can optionally specify which kernel instance(s) to match “kernel:{ip1,ip2,…} syntax.
- Parameters
name – Name to match against, prefixed with kernel name
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::ip objects that are compute units of this kernel object and matches the specified name.
-
ip get_ip(const std::string &name) const¶
get_ip() - Get a specific IP from the xclbin
The returned xrt::xclbin::ip object is extracted from the IP_LAYOUT section of the xclbin.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::ip objects from xclbin.
-
std::vector<mem> get_mems() const¶
get_mems() - Get list of memory objects
The returned xrt::xclbin::mem objects are extracted from the xclbin.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::mem objects from xclbin
-
std::string get_xsa_name() const¶
get_xsa_name() - Get Xilinx Support Archive (XSA) name of xclbin
An exception is thrown if the data is missing.
- Returns
Name of XSA (vbnv name).
-
std::string get_fpga_device_name() const¶
get_fpga_device_name() - Get FPGA device name
- Returns
Name of fpga device per XML metadata.
-
uuid get_uuid() const¶
get_uuid() - Get the uuid of the xclbin
An exception is thrown if the data is missing.
- Returns
UUID of xclbin
-
uuid get_interface_uuid() const¶
get_interface_uuid() - Get the interface uuid of the xclbin
An exception is thrown if the data is missing.
- Returns
Interface uuid of the xclbin
-
target_type get_target_type() const¶
get_target_type() - Get the type of this xclbin
- Returns
Target type, which can be hw, sw_emu, or hw_emu
-
class arg : public detail::pimpl<arg_impl>¶
class arg - xrt::xclbin::arg represents a compute unit argument
The argument object constructed from the xclbin connectivity section. An argument is connected to a memory bank or a memory group, which dictates where in device memory a global buffer used with this kernel argument must be allocated.
Public Functions
-
std::string get_name() const¶
get_name() - Get argument name
- Returns
Name of argument.
-
std::vector<mem> get_mems() const¶
get_mems() - Get list of device memories from xclbin.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::mem objects to which this argument is connected.
-
std::string get_port() const¶
get_port() - Get port name of this argument
- Returns
Port name
-
uint64_t get_size() const¶
get_size() - Argument size in bytes
- Returns
Argument size
-
uint64_t get_offset() const¶
get_offset() - Argument offset
- Returns
Argument offset
-
std::string get_host_type() const¶
get_host_type() - Get the argument host type
- Returns
Argument host type
-
size_t get_index() const¶
get_index() - Get the index of this argument
- Returns
Argument index
-
std::string get_name() const¶
-
class ip : public detail::pimpl<ip_impl>¶
xrt::xclbin::ip represents a IP in an xclbin.
The ip corresponds to an entry in the IP_LAYOUT section of the xclbin.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
std::string get_name() const¶
get_name() - Get name of IP
- Returns
IP name.
-
ip_type get_type() const¶
get_type() - Get the IP type
- Returns
IP type
-
control_type get_control_type() const¶
get_control_type() - Get the IP control protocol
- Returns
Control type
-
size_t get_num_args() const¶
get_num_args() - Number of arguments
- Returns
Number of arguments for this IP per CONNECTIVITY section
-
std::vector<arg> get_args() const¶
get_args() - Get list of IP arguments
An argument may have multiple memory connections
- Returns
A list sorted of xclbin::arg sorted by argument indices
-
arg get_arg(int32_t index) const¶
get_arg() - Get argument at index.
The argument may have multiple memory connections
- Parameters
index – Index of argument
- Returns
The argument a specified index
-
uint64_t get_base_address() const¶
get_base_address() - Get the base address of the cu
- Returns
The base address of the IP
-
size_t get_size() const¶
get_size() - Get the address range size of this IP.
The address range is a property of the kernel and as such only valid for for kernel compute units.
For IPs that are not associated with a kernel, the size return is 0.
- Returns
The size of this IP
-
std::string get_name() const¶
-
class kernel : public detail::pimpl<kernel_impl>¶
Public Functions
-
std::string get_name() const¶
get_name() - Get kernel name
- Returns
The name of the kernel
-
std::vector<ip> get_cus() const¶
get_cus() - Get list of cu from kernel.
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::ip objects corresponding the compute units for this kernel object.
-
std::vector<ip> get_cus(const std::string &name) const¶
get_cus() - Get list of compute units that matches name
The kernel name can optionally specify which kernel instance(s) to match “kernel:{cu1,cu2,…} syntax.
- Parameters
name – Name to match against, prefixed with kernel name
- Returns
A list of xrt::xclbin::ip objects that are compute units of this kernel object and matches the specified name.
-
ip get_cu(const std::string &name) const¶
get_cu() - Get compute unit by name
- Returns
The xct::xclbin::ip object matching the specified name, or error if not present.
-
size_t get_num_args() const¶
get_num_args() - Number of arguments
- Returns
Number of arguments for this kernel.
-
std::vector<arg> get_args() const¶
get_args() - Get list of kernel arguments
An argument may have multiple memory connections
- Returns
A list sorted of xclbin::arg sorted by argument indices
-
arg get_arg(int32_t index) const¶
get_arg() - Get kernel argument at index.
The memory connections of an argument is the union of the connections for each compute unit for that particular argument. In other words, for each connection of the argument returned by
get_arg()there is at least one compute unit that has that connection.- Returns
The xrt::xclbin::arg object at specified argument index.
-
std::string get_name() const¶
-
class mem : public detail::pimpl<mem_impl>¶
xrt::xclbin::mem represents a physical device memory bank
A memory object is constructed from an entry in the MEM_TOPOLOGY section of an xclbin.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
std::string get_tag() const¶
get_name() - Get tag name
- Returns
Memory tag name
-
uint64_t get_base_address() const¶
get_base_address() - Get the base address of the memory bank
- Returns
Base address of the memory bank, or -1 for invalid base address
-
uint64_t get_size_kb() const¶
get_size() - Get the size of the memory in KB
- Returns
Size of memory in KB, or -1 for invalid size
-
bool get_used() const¶
get_used() - Get used status of the memory
A value of false indicates that no buffer can be allocated in this memory bank.
- Returns
True of this memory bank is used by kernels in the xclbin or false otherwise.
-
memory_type get_type() const¶
get_type() - Get the type of the memory
- Returns
Memory type
-
int32_t get_index() const¶
get_index() - Get the index of the memory
The returned index can be used when allocating buffers using xrt::bo provided the memory bank is connected / used.
- Returns
Index of the memory within the memory topology
-
std::string get_tag() const¶
-
explicit xclbin(const std::string &filename)¶
XRT Native Library C API¶
Buffer APIs¶
- typedef xrtDeviceHandle
opaque device handle
- typedef xrtBufferHandle
opaque buffer handle
- typedef xrtBufferFlags
flags for BO
Description
See xrt_mem.h for available flags
- typedef xrtMemoryGroup
Memory bank group for buffer
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtBufferHandle xrtBOAllocUserPtr (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, void * userptr, size_t size, xrtBufferFlags flags, xrtMemoryGroup grp)
Allocate a BO using userptr provided by the user
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlDevice handle
void * userptrPointer to 4K aligned user memory
size_t sizeSize of buffer
xrtBufferFlags flagsSpecify type of buffer
xrtMemoryGroup grpSpecify bank information
Return
xrtBufferHandle on success or NULL
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtBufferHandle xrtBOAlloc (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, size_t size, xrtBufferFlags flags, xrtMemoryGroup grp)
Allocate a BO of requested size with appropriate flags
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlDevice handle
size_t sizeSize of buffer
xrtBufferFlags flagsSpecify type of buffer
xrtMemoryGroup grpSpecify bank information
Return
xrtBufferHandle on success or NULL
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtBufferHandle xrtBOImport (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, xclBufferExportHandle ehdl)
Allocate a BO imported from another device
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlDevice that imports the exported buffer
xclBufferExportHandle ehdlExported buffer handle, implementation specific type
Description
The exported buffer handle is acquired by using the export() method
and can be passed to another process.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xclBufferExportHandle xrtBOExport (xrtBufferHandle bhdl)
Export this buffer
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
Return
Exported buffer handle
An exported buffer can be imported on another device by this process or another process.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtBufferHandle xrtBOSubAlloc (xrtBufferHandle parent, size_t size, size_t offset)
Allocate a sub buffer from a parent buffer
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle parentParent buffer handle
size_t sizeSize of sub buffer
size_t offsetOffset into parent buffer
Return
xrtBufferHandle on success or NULL
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtBOFree (xrtBufferHandle bhdl)
Free a previously allocated BO
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
Return
0 on success, or err code on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC size_t xrtBOSize (xrtBufferHandle bhdl)
Get the size of this buffer
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
Return
Size of buffer in bytes
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC uint64_t xrtBOAddress (xrtBufferHandle bhdl)
Get the physical address of this buffer
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
Return
Device address of this BO, or LLONG_MAX on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtBOSync (xrtBufferHandle bhdl, enum xclBOSyncDirection dir, size_t size, size_t offset)
Synchronize buffer contents in requested direction
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBufferhandle
enum xclBOSyncDirection dirTo device or from device
size_t sizeSize of data to synchronize
size_t offsetOffset within the BO
Return
0 on success or error
Synchronize the buffer contents between host and device. Depending on the memory model this may require DMA to/from device or CPU cache flushing/invalidation
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC void* xrtBOMap (xrtBufferHandle bhdl)
Memory map BO into user’s address space
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
Return
Memory mapped buffer, or NULL on error
Map the contents of the buffer object into host memory. The buffer object is unmapped when freed.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtBOWrite (xrtBufferHandle bhdl, const void * src, size_t size, size_t seek)
Copy-in user data to host backing storage of BO
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
const void * srcSource data pointer
size_t sizeSize of data to copy
size_t seekOffset within the BO
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
Copy host buffer contents to previously allocated device
memory. seek specifies how many bytes to skip at the beginning
of the BO before copying-in size bytes of host buffer.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtBORead (xrtBufferHandle bhdl, void * dst, size_t size, size_t skip)
Copy-out user data from host backing storage of BO
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle bhdlBuffer handle
void * dstDestination data pointer
size_t sizeSize of data to copy
size_t skipOffset within the BO
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
Copy contents of previously allocated device memory to host
buffer. skip specifies how many bytes to skip from the
beginning of the BO before copying-out size bytes of device
buffer.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtBOCopy (xrtBufferHandle dst, xrtBufferHandle src, size_t sz, size_t dst_offset, size_t src_offset)
Deep copy BO content from another buffer
Parameters
xrtBufferHandle dstDestination BO to copy to
xrtBufferHandle srcSource BO to copy from
size_t szSize of data to copy
size_t dst_offsetOffset into destination buffer to copy to
size_t src_offsetOffset into src buffer to copy from
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
It is an error if sz is 0 bytes or sz + src/dst_offset is out of bounds.
Configuration APIs¶
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtIniStringSet (const char * key, const char * value)
Change xrt.ini string value for specified key
Parameters
const char * keyKey to change value for
const char * valueNew value for key
Return
0 on success, error if key value cannot be changed
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtIniUintSet (const char * key, unsigned int value)
Change xrt.ini unsigned int value for specified key
Parameters
const char * keyKey to change value for
unsigned int valueNew value for key
Return
0 on success, error if key value cannot be changed
Device and XCLBIN APIs¶
- typedef xrtDeviceHandle
opaque device handle
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtDeviceHandle xrtDeviceOpen (unsigned int index)
Open a device and obtain its handle
Parameters
unsigned int indexDevice index
Return
Handle representing the opened device, or nullptr on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtDeviceHandle xrtDeviceOpenByBDF (const char * bdf)
Open a device and obtain its handle
Parameters
const char * bdfPCIe BDF identifying the device to open
Return
Handle representing the opened device, or nullptr on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtDeviceHandle xrtDeviceOpenFromXcl (xclDeviceHandle xhdl)
Open a device from a shim xclDeviceHandle
Parameters
xclDeviceHandle xhdlShim xclDeviceHandle
Return
Handle representing the opened device, or nullptr on error
The returned XRT device handle must be explicitly closed when nolonger needed.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceClose (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl)
Close an opened device
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
Return
0 on success, error otherwise
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceLoadXclbin (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, const struct axlf * xclbin)
Load an xclbin image
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
const struct axlf * xclbinPointer to complete axlf in memory image
Return
0 on success, error otherwise
The xclbin image can safely be deleted after calling this funciton.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceLoadXclbinFile (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, const char * xclbin_fnm)
Read and load an xclbin file
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
const char * xclbin_fnmFull path to xclbin file
Return
0 on success, error otherwise
This function read the file from disk and loads the xclbin. Using this function allows one time allocation of data that needs to be kept in memory.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceLoadXclbinHandle (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, xrtXclbinHandle xhdl)
load an xclbin from an xrt::xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlxrt::xclbin handle
Return
0 on success, error otherwise
This function uses the specified xrt::xclbin object created by caller. The xrt::xclbin object must contain the complete axlf structure.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceLoadXclbinUUID (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, const xuid_t uuid)
load an xclbin from an xrt::xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
const xuid_t uuiduuid_t struct of xclbin id
Return
0 on success, error otherwise
This function reads the xclbin id already loaded in the system and comapres it with the input uuid. If they match, load the cached xclbin metadata into caller’s process. Otherwise returns error.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtDeviceGetXclbinUUID (xrtDeviceHandle dhdl, xuid_t out)
Get UUID of xclbin image loaded on device
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle dhdlHandle to device previously opened with xrtDeviceOpen
xuid_t outReturn xclbin id in this uuid_t struct
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
Note that current UUID can be different from the UUID of the xclbin loaded by this process using load_xclbin()
- typedef xrtXclbinHandle
opaque xclbin handle
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtXclbinHandle xrtXclbinAllocFilename (const char * filename)
Allocate a xclbin using xclbin filename
Parameters
const char * filenamepath to the xclbin file
Return
xrtXclbinHandle on success or NULL with errno set
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtXclbinHandle xrtXclbinAllocAxlf (const struct axlf * top_axlf)
Allocate a xclbin using an axlf
Parameters
const struct axlf * top_axlfan axlf
Return
xrtXclbinHandle on success or NULL with errno set
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtXclbinHandle xrtXclbinAllocRawData (const char * data, int size)
Allocate a xclbin using raw data
Parameters
const char * dataraw data buffer of xclbin
int sizesize (in bytes) of raw data buffer of xclbin
Return
xrtXclbinHandle on success or NULL with errno set
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtXclbinFreeHandle (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl)
Deallocate the xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlxclbin handle
Return
0 on success, -1 on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtXclbinGetXSAName (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl, char * name, int size, int * ret_size)
Get Xilinx Support Archive (XSA) Name of xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlXclbin handle
char * nameReturn name of XSA. If the value is nullptr, the content of this value will not be populated. Otherwise, the the content of this value will be populated.
int sizesize (in bytes) of name.
int * ret_sizeReturn size (in bytes) of XSA name. If the value is nullptr, the content of this value will not be populated. Otherwise, the the content of this value will be populated.
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtXclbinGetUUID (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl, xuid_t ret_uuid)
Get UUID of xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlXclbin handle
xuid_t ret_uuidReturn xclbin id in this uuid_t struct
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC size_t xrtXclbinGetNumKernels (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl)
Get number of PL kernels in xclbin
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlXclbin handle obtained from an xrtXclbinAlloc function
Return
The number of PL kernels in the xclbin
Kernels are extracted from embedded XML metadata in the xclbin. A kernel groups one or more compute units. A kernel has arguments from which offset, type, etc can be retrived.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC size_t xrtXclbinGetNumKernelComputeUnits (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl)
Get number of CUs in xclbin
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlXclbin handle obtained from an xrtXclbinAlloc function
Return
The number of compute units
Compute units are associated with kernels. This function returns the total number of compute units as the sum of compute units over all kernels.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtXclbinGetData (xrtXclbinHandle xhdl, char * data, int size, int * ret_size)
Get the raw data of the xclbin handle
Parameters
xrtXclbinHandle xhdlXclbin handle
char * dataReturn raw data. If the value is nullptr, the content of this value will not be populated. Otherwise, the the content of this value will be populated.
int sizeSize (in bytes) of data
int * ret_sizeReturn size (in bytes) of XSA name. If the value is nullptr, the content of this value will not be populated. Otherwise, the the content of this value will be populated.
Return
0 on success or appropriate error number
Kernel APIs¶
- typedef xrtKernelHandle
opaque kernel handle
Description
A kernel handle is obtained by opening a kernel. Clients pass this kernel handle to APIs that operate on a kernel.
- typedef xrtRunHandle
opaque handle to a specific kernel run
Description
A run handle is obtained by running a kernel. Clients use a run handle to check or wait for kernel completion.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtKernelHandle xrtPLKernelOpen (xrtDeviceHandle deviceHandle, const xuid_t xclbinId, const char * name)
Open a PL kernel and obtain its handle.
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle deviceHandleHandle to the device with the kernel
const xuid_t xclbinIdThe uuid of the xclbin with the specified kernel.
const char * nameName of kernel to open.
Return
Handle representing the opened kernel.
The kernel name must uniquely identify compatible kernel instances (compute units). Optionally specify which kernel instance(s) to open using “kernelname:{instancename1,instancename2,…}” syntax. The compute units are opened with shared access, meaning that other kernels and other process will have shared access to same compute units. If exclusive access is needed then open the kernel using xrtPLKernelOpenExclusve().
An xclbin with the specified kernel must have been loaded prior to calling this function. An XRT_NULL_HANDLE is returned on error and errno is set accordingly.
A kernel handle is thread safe and can be shared between threads.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtKernelHandle xrtPLKernelOpenExclusive (xrtDeviceHandle deviceHandle, const xuid_t xclbinId, const char * name)
Open a PL kernel and obtain its handle.
Parameters
xrtDeviceHandle deviceHandleHandle to the device with the kernel
const xuid_t xclbinIdThe uuid of the xclbin with the specified kernel.
const char * nameName of kernel to open.
Return
Handle representing the opened kernel.
Same as xrtPLKernelOpen(), but opens compute units with exclusive access. Fails if any compute unit is already opened with either exclusive or shared access.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtKernelClose (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle)
Close an opened kernel
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to kernel previously opened with xrtKernelOpen
Return
0 on success, -1 on error
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtKernelArgGroupId (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle, int argno)
Acquire bank group id for kernel argument
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to kernel previously opened with xrtKernelOpen
int argnoIndex of kernel argument
Return
Group id or negative error code on error
A valid group id is a non-negative integer. The group id is required when constructing a buffer object.
The kernel argument group id is ambigious if kernel has multiple kernel with different connectivity for specified argument. In this case the API returns error.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC uint32_t xrtKernelArgOffset (xrtKernelHandle khdl, int argno)
Get the offset of kernel argument
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle khdlHandle to kernel previously opened with xrtKernelOpen
int argnoIndex of kernel argument
Return
The kernel register offset of the argument with specified index
Use with :c:func:`xrtKernelReadRegister()` and :c:func:`xrtKernelWriteRegister()`
if manually reading or writing kernel registers for explicit arguments.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtKernelReadRegister (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle, uint32_t offset, uint32_t * datap)
Read data from kernel address range
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to kernel previously opened with xrtKernelOpen
uint32_t offsetOffset in register space to read from
uint32_t * datapPointer to location where to write data
Return
0 on success, errcode otherwise
The kernel must be associated with exactly one kernel instance (compute unit), which must be opened for exclusive access.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtKernelWriteRegister (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle, uint32_t offset, uint32_t data)
Write to the address range of a kernel
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to kernel previously opened with xrtKernelOpen
uint32_t offsetOffset in register space to write to
uint32_t dataData to write
Return
0 on success, errcode otherwise
The kernel must be associated with exactly one kernel instance (compute unit), which must be opened for exclusive access.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtRunHandle xrtKernelRun (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle, ...)
Start a kernel execution
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to the kernel to run
...Kernel arguments
Return
Run handle which must be closed with xrtRunClose()
A run handle is specific to one execution of a kernel. Once
execution completes, the run handle can be re-used to execute the
same kernel again. When no longer needed, then run handle must be
closed with xrtRunClose().
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC xrtRunHandle xrtRunOpen (xrtKernelHandle kernelHandle)
Open a new run handle for a kernel without starting kernel
Parameters
xrtKernelHandle kernelHandleHandle to the kernel to associate the run handle with
Return
Run handle which must be closed with xrtRunClose()
The handle can be used repeatedly to start an execution of the associated kernel. This API allows application to manage run handles without maintaining corresponding kernel handle.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtRunSetArg (xrtRunHandle rhdl, int index, ...)
Set a specific kernel argument for this run
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to the run object to modify
int indexIndex of kernel argument to set
...The argument value to set.
Return
0 on success, -1 on error
Use this API to explicitly set specific kernel arguments prior
to starting kernel execution. After setting all arguments, the
kernel execution can be start with xrtRunStart()
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtRunUpdateArg (xrtRunHandle rhdl, int index, ...)
Asynchronous update of kernel argument
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to the run object to modify
int indexIndex of kernel argument to update
...The argument value to update.
Return
0 on success, -1 on error
Use this API to asynchronously update a specific kernel argument of an existing run.
This API is only supported on Edge.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtRunStart (xrtRunHandle rhdl)
Start existing run handle
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to the run object to start
Return
0 on success, -1 on error
Use this API when re-using a run handle for more than one execution of the kernel associated with the run handle.
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC enum ert_cmd_state xrtRunWait (xrtRunHandle rhdl)
Wait for a run to complete
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to the run object to start
Return
- Run command state for completed run,
or ERT_CMD_STATE_ABORT on error
Blocks current thread until job has completed
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC enum ert_cmd_state xrtRunWaitFor (xrtRunHandle rhdl, unsigned int timeout_ms)
Wait for a run to complete
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to the run object to start
unsigned int timeout_msTimeout in millisecond
Return
- Run command state for completed run, or
current status if timeout.
Blocks current thread until job has completed
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC enum ert_cmd_state xrtRunState (xrtRunHandle rhdl)
Check the current state of a run
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to check
Return
The underlying command execution state per ert.h
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtRunSetCallback (xrtRunHandle rhdl, enum ert_cmd_state state, void (*callback) (xrtRunHandle, enum ert_cmd_state, void*, void * data)
Set a callback function
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to set callback on
enum ert_cmd_state stateState to invoke callback on
void (*)(xrtRunHandle, enum ert_cmd_state, void*) callbackCallback function
void * dataUser data to pass to callback function
Description
Register a run callback function that is invoked when the run changes underlying execution state to specified state. Support states are: ERT_CMD_STATE_COMPLETED (to be extended)
- XCL_DRIVER_DLLESPEC int xrtRunClose (xrtRunHandle rhdl)
Close a run handle
Parameters
xrtRunHandle rhdlHandle to close
Return
0 on success, -1 on error