OpenAMP on Kria SOM¶
Starting from 2022.1, OpenAMP support is available for the AMD Kria™ SOM prebuilt images. OpenAMP is an open-source standard infrastructure for applications to make use of heterogeneous coprocessors and in Kria, allows the APU to offload tasks to the MPSoC dual-core RPUs.
The Kria Starter Kit OpenAMP PetaLinux implementation uses the Linux kernel implementation of RPMsg for leveraging the MPSoC RPUs as coprocessors. The out-of-box Kria Linux OpenAMP only implements a Linux based master on the APU with the RPU as a client processor with corresponding prebuilt RPU examples.
RPMsg Implementation¶
The OpenAMP community supports two models for RPMsg in a Linux master environment:
Linux kernel and RPU remote CPU
RPMsg uses kernel integrated rpmsg and virtio implementations. The Kria implementation does not make use of the Libmetal or OpenAMP libraries in the Linux domain.
The Linux kernel space provides rpmsg and remoteproc, but the RPU application requires Linux to load it to talk to the RPMsg counterpart in the Linux kernel.
Linux userspace OpenAMP application and RPU remote CPU
Linux rpmsg is implemented using the libmetal library with a userspace implementation of virtio
OpenAMP library can also be used in a Linux userspace. In this configuration, the remote processor can run independently to the Linux host processor.
The Kria Starter Kit Linux OpenAMP solution uses a Linux kernel implementation (item #1). Details are shown in the following block diagram from the Libmetal and OpenAMP User Guide ([UG1186])https://docs.amd.com/go/en-US/ug1186-zynq-openamp-gsg.
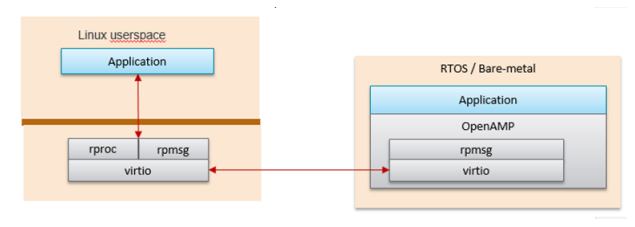
OpenAMP Device Tree¶
The Kria Starter Kit Linux includes the following device tree placeholders for OpenAMP coprocessing applications:
remoteproc node
rpmsg shared memory
The Kria 2022.1 PetaLinux BSP and prebuilt images folder include the necessary device tree nodes and memory reservations. These can be found in the openamp.dtb of the 2022.1 release BSP prebuilt folder. To run the OpenAMP example, program the SD card with the prebuilt .wic image, and replace system.dtb in the SD card’s boot folder with openamp.dtb (which should be renamed to system.dtb), and boot as usual.
OpenAMP Demos¶
The 2022.1 (and onward) the based Kria Starter Kit Linux BSP contains support for the existing OpenAMP community demos summarized as follows.
openamp-echo-test: Linux to RPU baremetal communication echo test using rpsmsg.
openamp-matrix-mul: Linux produces two matrices and sends them to the RPU for multiplication.
openamp-rpc-demo: Shows the proxy behavior of the RPU as a coprocessor to the APU.
Details about each example applications can be found in the Libmetal and OpenAMP User Guide ([UG1186])<https://docs.amd.com/go/en-US/ug1186-zynq-openamp-gsg/OpenAMP-Demos>.
In 2022.1 and 2022.2, the PetaLinux BSPs with OpenAMP support require system.dtb to be replaced with openamp.dtb on the SD boot partition. The required .wic image and openamp.dtb are included in BSPs.
In 2023.1 and newer, both Yocto built PetaLinux and BSP based PetaLinux has OpenAMP packages available for installation on target. To download support, do the following on target:
sudo dnf install open-amp-device-tree
sudo dnf install packagegroup-petalinux-openamp-echo-test
sudo dnf install packagegroup-petalinux-openamp-matrix-mul
sudo dnf install packagegroup-petalinux-openamp-rpc-demo
sudo reboot
A reboot is required to pick up the OpenAMP device tree.
To run the OpenAMP applications, reference the following commands. The echo start and end stop commands are required for each execution of the example application.
Echo Test application:
sudo -s # This is required so that the ELF loading can occur.
echo image_echo_test > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware # Specify Echo Test Firmware to be loaded.
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Load and start target Firmware onto remote processor.
echo_test # Run echo test linux application.
echo stop > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Stop target firmware.
Output of Echo Test should look like this:
**************************************
Echo Test Round 0
**************************************
sending payload number 0 of size 17
echo test: sent : 17
received payload number 0 of size 17
sending payload number 1 of size 18
echo test: sent : 18
received payload number 1 of size 18
.
.
.
sending payload number 470 of size 487
echo test: sent : 487
received payload number 470 of size 487
sending payload number 471 of size 488
echo test: sent : 488
received payload number 471 of size 488
******************
18 L6 rpmsg_endpoint_cb():36 shutdown message is received.
19 L7 app():82 done
20 L6 main():129 Stopping application...
21 L7 unregistered generic bus
********************
Echo Test Round 0 Test Results: Error count = 0
**************************************
xilinx-kv260-starterkit-20221:/home/petalinux#
Matrix Multiplication:
sudo -s # This is required so that the ELF loading can occur.
echo image_matrix_multiply > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware # Specify Matrix multiplication to get Firmare onto remote processor.
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Load and start target Firmware onto remote processor.
mat_mul_demo # Run Matrix multiplication test linux application.
echo stop > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Stop target firmware.
Proxy RPC application:
Output of Matrix Multiplication should look like this:
Master : Linux : Input matrix 0
8 7 8 6 7 9
7 5 1 5 2 8
7 5 9 9 9 0
9 0 6 5 2 2
1 2 1 2 8 7
8 7 6 6 5 3
Master : Linux : Input matrix 1
7 2 0 0 0 4
8 7 1 9 8 0
1 7 3 7 4 5
0 6 7 1 8 6
0 8 5 8 6 0
3 5 4 3 6 4
0: write rpmsg: 296 bytes
read results
Master : Linux : Printing results
147 258 144 208 232 144
114 142 85 97 144 95
98 238 140 189 202 127
75 116 71 69 88 104
45 134 87 112 126 49
127 198 104 160 176 110
End of Matrix multiplication demo Round 0
Quitting application ..
Matrix multiply application end
Proxy Application:
sudo -s # This is required so that the ELF loading can occur.
echo image_rpc_demo > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware # Specify proxy application to get Firmare onto remote processor.
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Load and start target Firmware onto remote processor.
proxy_app # Run proxy application.
echo stop > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state # Stop target firmware
Expected output of Proxy Application:
Master>RPC service started !!
Remote>Baremetal Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Demonstration
Remote>***************************************************
Remote>Rpmsg based retargetting to proxy initialized..
Remote>FileIO demo ..
Remote>Creating a file on master and writing to it..
Remote>Opened file 'remote.file' with fd = 6
Remote>Wrote to fd = 6, size = 45, content = This is a test string being written to file..
Remote>Closed fd = 6
Remote>Reading a file on master and displaying its contents..
Remote>Opened file 'remote.file' with fd = 6
handle_read: 4, 225
Remote>Read from fd = 6, size = 225, printing contents below .. This is a test string being written to file..This is a test string being written to file..This is a test string being written to file..This is a test string being written to file..This is a test string being written to file..
Remote>Closed fd = 6
Remote>Remote firmware using scanf and printf ..
Remote>Scanning user input from master..
Remote>Enter name
Jane
handle_read: 4, 4
Remote>Enter age
29
handle_read: 4, 3
Remote>Enter value for pi
3.14
handle_read: 4, 5
Remote>User name = 'Jane'
Remote>User age = '29'
Remote>User entered value of pi = '3.140000'
Remote>Repeat demo ? (enter yes or no)
no
handle_read: 4, 3
Remote>RPC retargetting quitting ...
Remote> Firmware's rpmsg-rpc-channel going down!