Resize Down¶
Overview¶
The resize refers to the resizing of a digital image, but resize kernel only can process one channel of XYB. And our resize based on bicubic interpolation what is an extension of cubic interpolation for interpolating data points on a two demensional regular grid. Image resampled with bicubic interpolation are smoother and have fewer interpolation artifacts. If you want to get more about bicubic interpolation, you can read more details from here.
Implementation¶
According to characteristic of bicubic interpolation, we get derivative int_{xy} by first calculating int_{y} and then int_{x} from those. And interpolator optimizated is a 8x acceleration compare with original algorithm using sliding window on FPGA. The implemention is shown in the figure below:
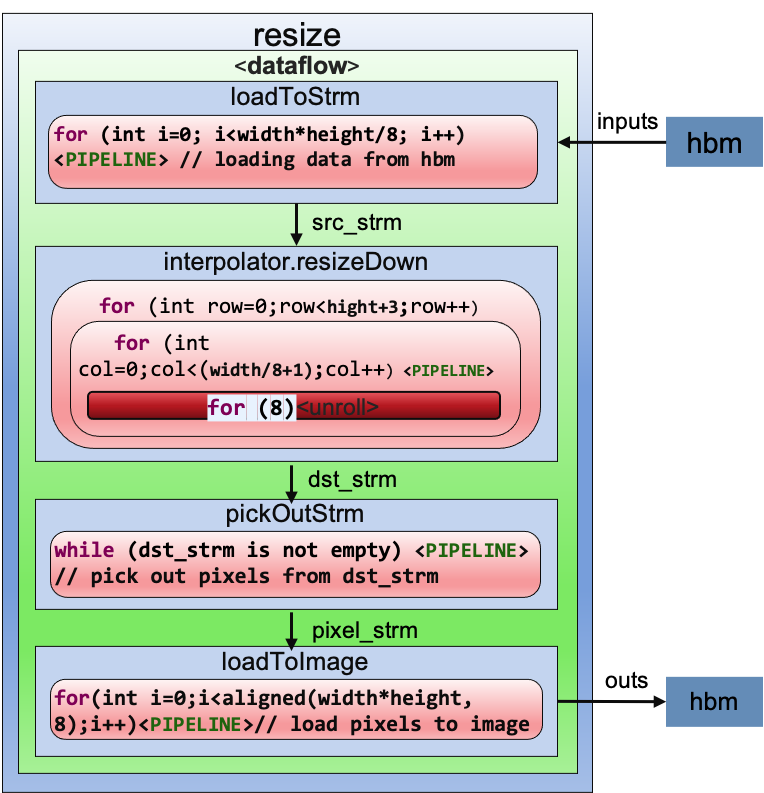
The kernel will do the following steps:
- Load data from HBM: Load the original image pixels to stream and eight-bits represents a pixel. If NPPC=1 refers one pixel processing for every clock and NPPC=8 refers eight pixels processing for every clock.
- Image resampling: In image processing, we apply cubic interpolation to a data set from sliding window which is our proposed a structure for image processing. Here we can process 8 pixels in a clock that we take full advantage of the features of URAM to support. We can get several(<=8) results using 8 interpolator with ervery eight pixels, and put these results into a stream.
- Pick out pixel: We would pick out real and effective pixels from a 72-bits unit and making up these pixels a 64-bits unit.
- Load output to HBM: Scan stream to get data and write back to HBM.
Interface¶
Currently, the input should be a channel of image and the pixel width is eight. This kernel can process a 8K image to smaller image.
The output is a resized down image which you want to be. The image surface is smoother than correponding surfaces obtained by bilinear interpolation or nearest-neighbor interpolation.