Internal Design of Strongly Connected Component¶
Overview¶
In the mathematical theory of directed graphs, a graph is said to be strongly connected if every vertex is reachable from every other vertex. The strongly connected components of an arbitrary directed graph form a partition into subgraphs that are themselves strongly connected. (from wikipedia) The API will compute the strongly connected component (SCC) of each vertex and return a graph with the vertex value containing the lowest vertex id in the SCC containing that vertex.
Algorithm¶
The color-based algorithm of strongly connected components is given as following:
procedure StronglyConnectedComponent(graph_CSR)
graph_CSC := csr2csc(graph_CSR)
for each vertex v in graph
result(v) := -1
color(v) := -1
while all vertexs have been labeled
FW-coloring(graph_CSR, FW-Queue, color)
BW-labeling(graph_CSR, graph_CSC, BW-Queue, color, result)
end while
return result
sub procedure FW-coloring(graph_CSR, FW-Queue, color)
rootNode := findNewRoot(FW-Queue, color)
push rootNode into FW-Queue
while FW-Queue is not empty
u := pop FW-Queue
for each edge(u, v) in graph_CSR
if color(v) == -1 then
color(v) = u
push v into FW-Queue
end if
end for
end while
sub procedure BW-labeling(graph_CSR, graph_CSC, FW-Queue, BW-Queue, color, result)
newRootNode := rootNode
result(rootNode) := rootNode
for v in this color region
if indegree(v) == 0 or outdegree(v) == 0 then
result(v) := v
end if
end for
while all vertexs in this color region have been labeled
push newRootNode into BW-Queue
while BW-Queue is not empty
u := pop BW-Queue
for each edge(u, v) in graph_CSC
if color(v) == newRootNode and result(v) == -1 then
result(v) = newRootNode
push v into BW-Queue
end if
end for
end while
if there is one more vertex which hasn't been labeled
Re-color those vertexs which aren't labeled in last BW-BFS into rootNode
newRootNode := FW-BFS(graph_CSR, BW-Queue, color)
FW-BFS(graph_CSR, BW-Queue, color)
end if
end while
Here, for color-based alogrithm, each backward label process must be started from the vertex whose color is equal to its vertex ID. In other words, the starting vertex must own the lowest vertex ID in the following SCC. As a result, we use one single FW-BFS process to find the starting vertex before each BW-label. And another FW-BFS is required to re-color using the true starting vertex if the first FW-BFS is started from one vertex with greater vertex ID.
Interface¶
The input should be a directed graph in compressed sparse row (CSR) format. The result will return a vertex list with each vertex value containing the lowest vertex id in the SCC.
Implemention¶
The detail algorithm implemention is shown as the figure below:
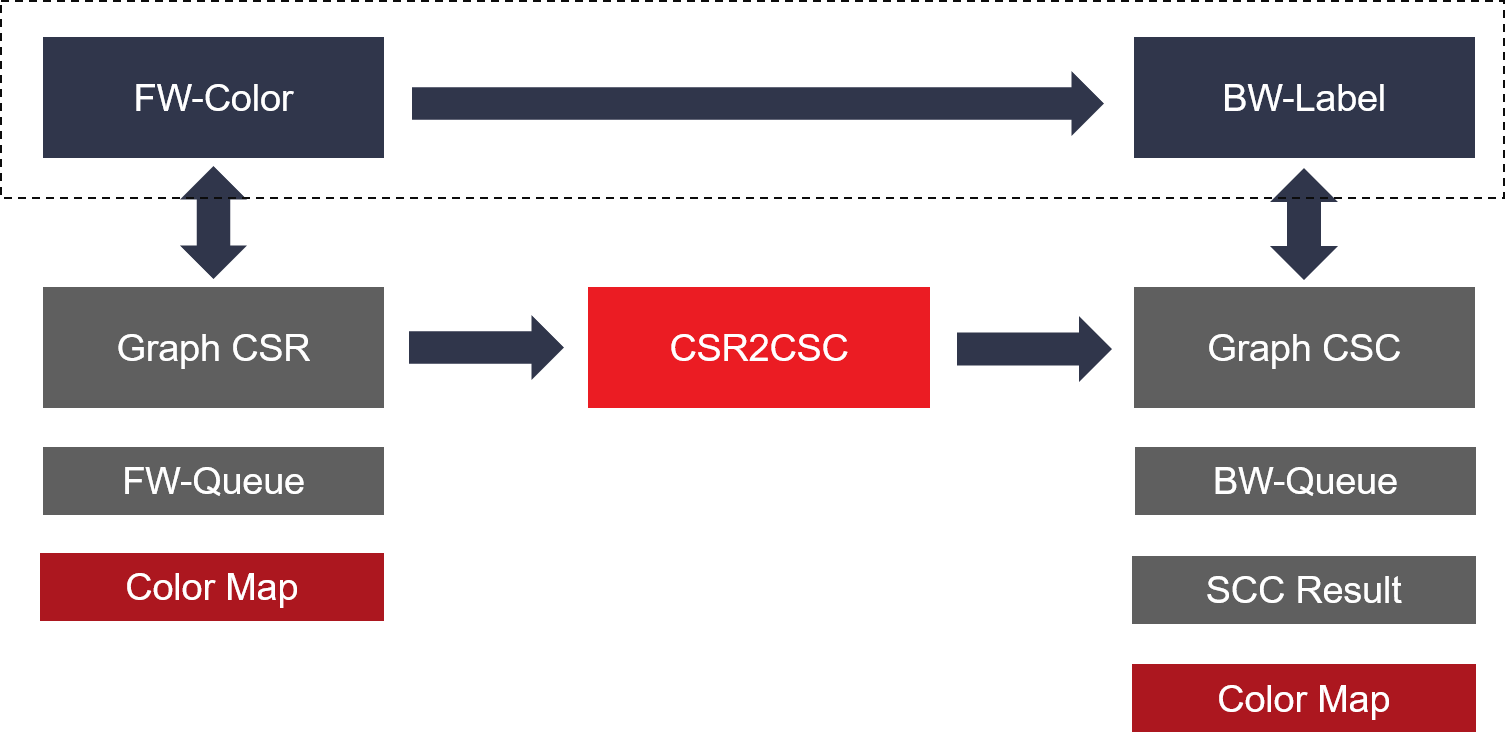
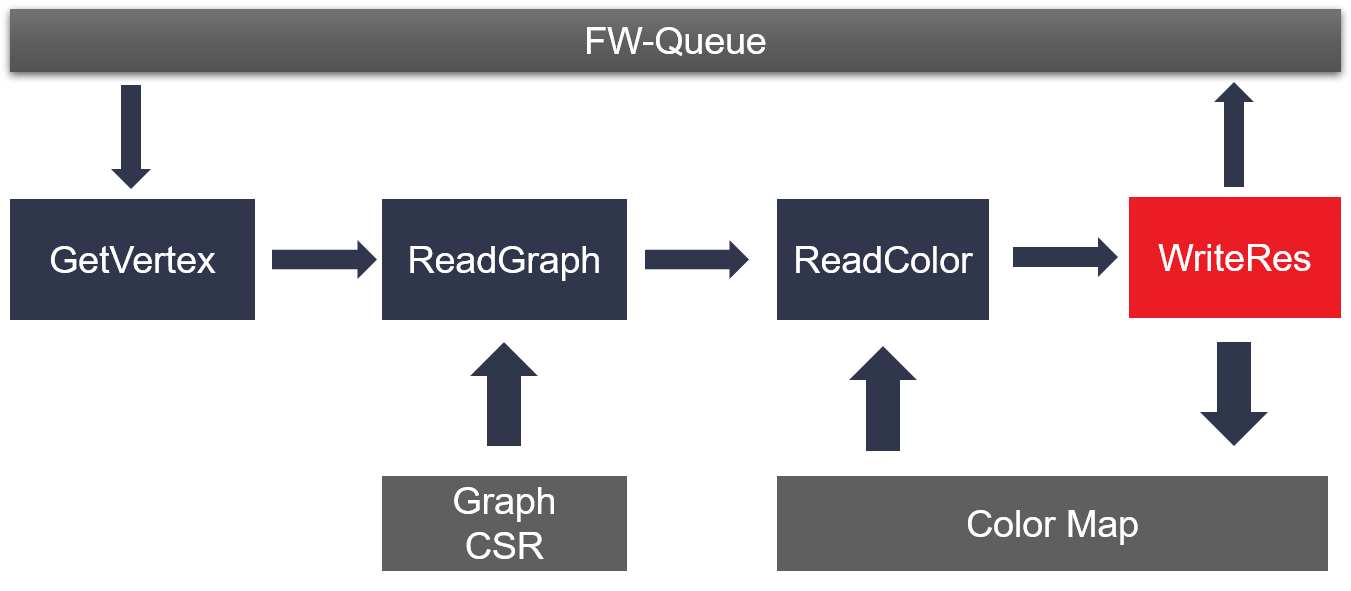
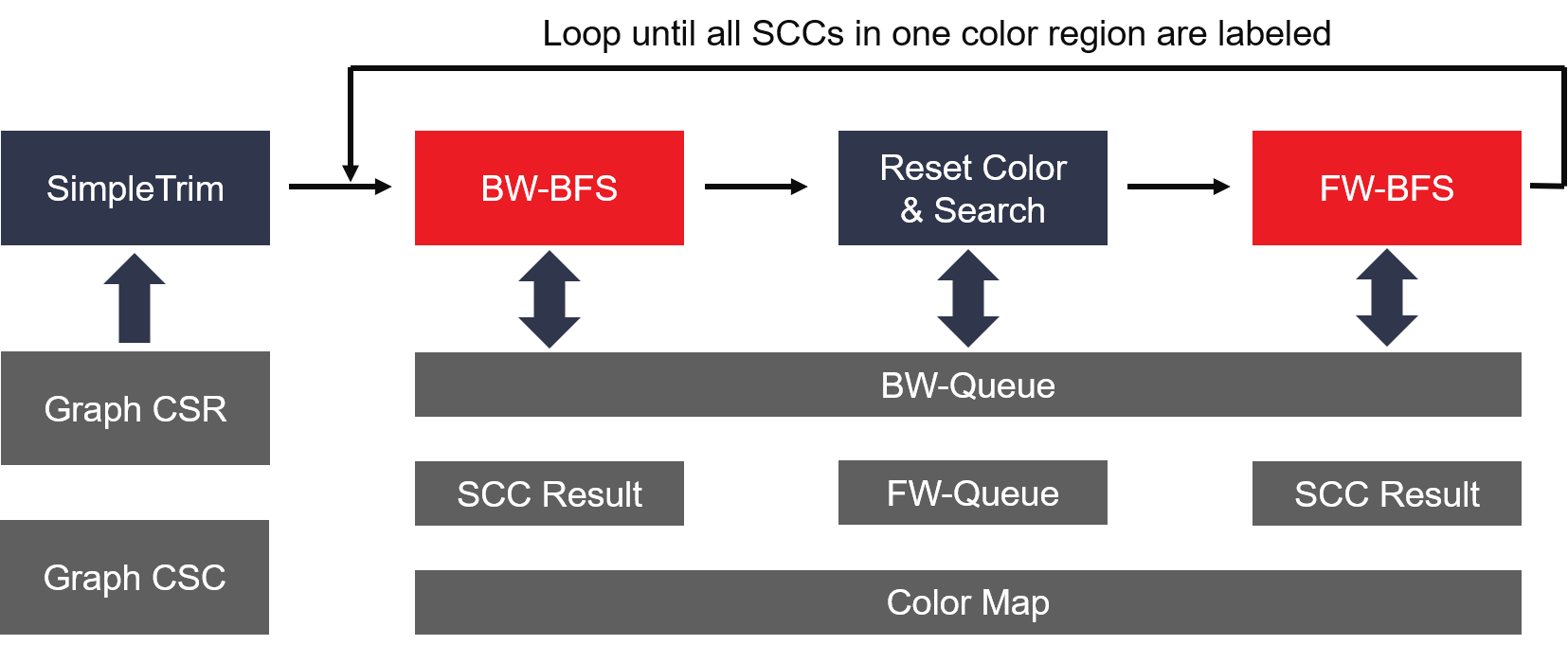
In the SCC kernel design, FW-color and BW-Label can be dataflow by sharing some common buffers with multiple independent AXI masters. As a result, these two processes will be run at the same time to obtain a better performance.
Profiling and Benchmarks¶
The kernel is built by Vivado tools and benchmard in U250 FPGA card at 275MHz. The hardware resource utilization and benchmark performance are listed in the table below.
| Name | LUT | BRAM | URAM | DSP |
| Platform | 104112 | 165 | 0 | 4 |
| scc_kernel | 164311 | 523.5 | 110 | 6 |
| Total | 268423 (16%) | 688.5 (26%) | 110 (9%) | 10 (0%) |
| Datasets | Vertex | Edges |
|
Iteration number in Spark | FPGA Time | Spark (4 threads) | Spark (8 threads) | Spark (16 threads) | Spark (32 threads) | ||||
| Spark Time | Speed up | Spark Time | Speed up | Spark Time | Speed up | Spark Time | Speed up | ||||||
| cit-Patents | 3774768 | 16518948 | 3774768 | 6 | 20711 | 52137 | 2.52 | 60517 | 2.92 | 51390 | 2.48 | 39939 | 1.93 |
| hollywood | 1139905 | 57515616 | 1139905 | 6 | 9780 | 75681 | 7.74 | 45935 | 4.70 | 39595 | 4.05 | 29665 | 3.03 |
| soc-LiveJournal1 | 4847571 | 68993773 | 971232 | 6 | 39952 | 424444 | 10.62 | 304755 | 7.63 | 244916 | 6.13 | 231465 | 5.79 |
| ljournal-2008 | 5363260 | 79023142 | 1119171 | 16 | 34840 | 540199 | 15.51 | 458633 | 13.16 | 378304 | 10.86 | 402120 | 11.54 |
| GEOMEAN | 23043 | 173431 | 7.53X | 140397 | 6.09X | 117178 | 5.09X | 102476 | 4.45X | ||||
Note
1. Spark running on platform with Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2690 v4 @2.600GHz, 56 Threads (2 Sockets, 14 Core(s) per socket, 2 Thread(s) per core)2. Time unit: ms.