Internal Design of Louvain Modularity¶
Overview¶
The Louvain method for community detection is a method to extract communities from large networks created by Blondel from the University of Louvain (the source of this method’s name). The method is a greedy optimization method that appears to run in time O(n cdot log n), if n is the number of nodes in the network. Since we release the louvain kernel on FPGA from 21.1, the performance of 1 compute unit in this kernel is improved from 18x, to 33x, to 65x vs CPU. The latest design cloud achieve 2 compute units in u55c by Vitis 22.1, which means the max speed up by u55c cloud be 2*65x vs CPU. Now the L2 API cloud achieve the entire graph louvain modularity directly. when the graph is less than 128M vertexes and 128M edges by 1 cu on u55c(64M is the limit by 1 cu on u50). If the graph is larger, we should launch the L3 louvainPartition API, partition the graph to multi pieces, then run the L3 louvainRun API which cloud run louvain algorithm on multi cu on multi board by the support of xrm. More details cloud be find in L3 API.
Algorithm¶
PageRank algorithm implementation:
Louvain(G(V, E, W), Cid)
Q_old := 0
Q_new := 0
Cid_new := C_init
ColorSets = Coloring(V)
while true // Iterate until modularity gain becomes negligible.
for each node Vk in ColorSets
Cid_old := Cid_new
for each v in Vk
vCid := Cid_old[v]
for each e in e \cup (v, E, W)
maxQ := max(\Delta Q)
target := Cid_old[e]
if maxQ > 0 then
Cid_new[v] = target
Q_new := Q(Cid_new)
if Q_new < Q_old then
break
else
Q_old = Q_new
return {Cid_old, Q_old}
- undirected graph
- compressed sparse column (COO) format
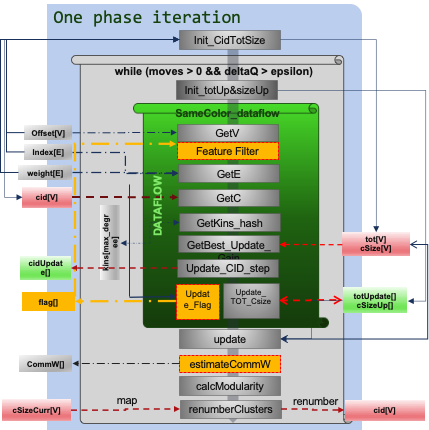
The algorithm implemention is shown as the figure below:
Figure 1 : Louvain calculate modularity architecture on FPGA