Internal Design of Minimum Spanning Tree¶
Overview¶
Minimum Spanning Tree is the problem of finding a set of edges that can connect all the vertices in a undirected graph with the minumal sum of edge weights.
Algorithm¶
The implemented Minimum Spanning Tree algorithm is based on the Prim algorithm. The description of the algorithm is as below:
Given an undirected graph, and a source vertex, print out a MST for the connected subgraph which contains the source vertex.
- Start with a set MSTNodes = {source vertex}
- For all vertices in MSTNodes, find another vertex y in the graph but not MSTNodes which is connected to a vertex x in MSTNodes such that the weight on the edge e(x,y) is the smallest among all such edges from a vertex in MSTNodes to a vertex not in MSTNodes. Add y to MSTNodes, and add the edge (x,y) to MST
- Repeat 2 until MSTNodes has no edge linking to any other vertex in the graph.
Interface¶
The input should be an undirected graph in compressed sparse row (CSR) format. The result is an array which shows the predecessor of a vertex in the generated tree. The vertex ID can be used to index the result array.
Implementation¶
The algorithm implemention is shown in the figure below:
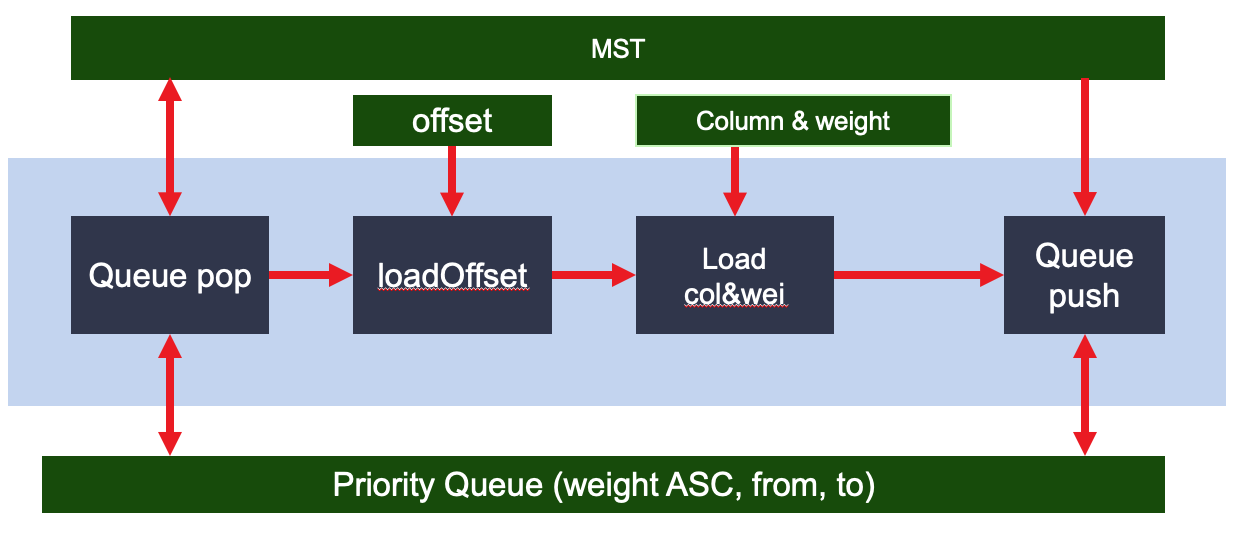
There are 4 functional blocks as shown in the figure:
- QueuePop is responsible to load the next vertex in the priority queue and pass it to the loadOffset.
- loadOffset loads the offset value associate with current vertex from the CSR offset values and pass it to the next block.
- loadCol&Wei loads the ID and weight of the next hop vertices according to the offset values. And it passes these IDs and weights to the loadRes.
- Queue pushes the next hop vertices into the priority queue. And it sorts the priority again.
This system starts from pushing the source vertex into the queue and iterate until the queue is empty.