The MD4/MD5 Message-Digest Algorithms¶
Overview¶
The MD4/MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm is a hash-based cryptographic function. It takes a message of arbitrary length as its input and produces a 128-bit digest. Both MD4 and MD5 have a padding and appending process before digest the message of arbitrary length. The difference between MD4 and MD5 is the digest process. The MD4 have 3 round hash calculations while the MD5 have 4. For each round, both of them have intra loop-carried dependencies.
Currently this library supports the following algorithms:
- MD4
- MD5
The MD4 algorithm is defined in RFC 1320, and the MD5 is defined in RFC 1321.
Implementation on FPGA¶
The internal structure of MD4 and MD5 are shown in the figures below:
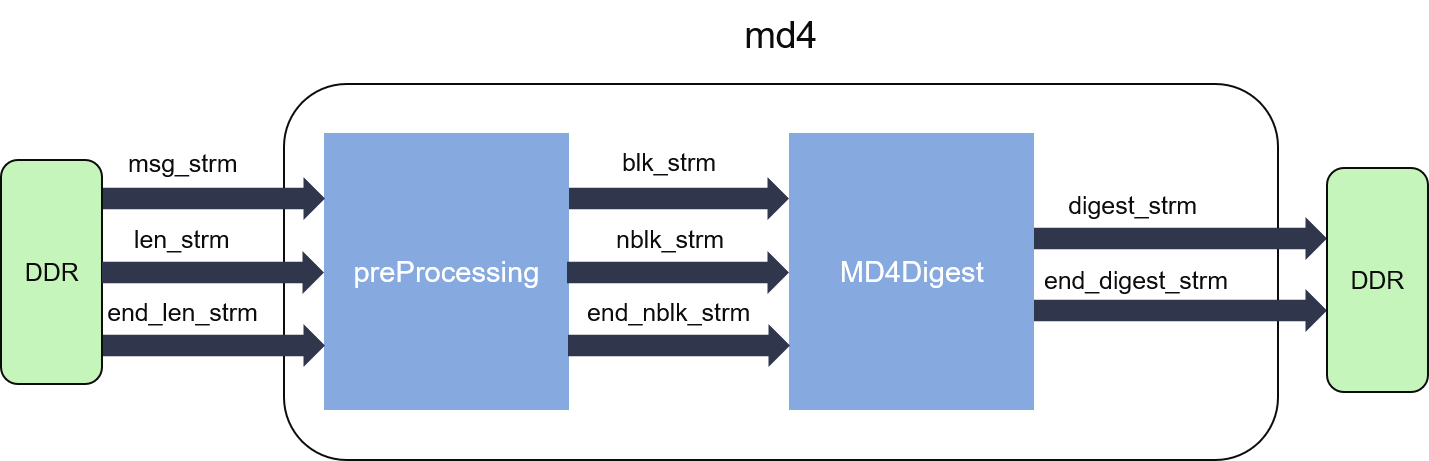
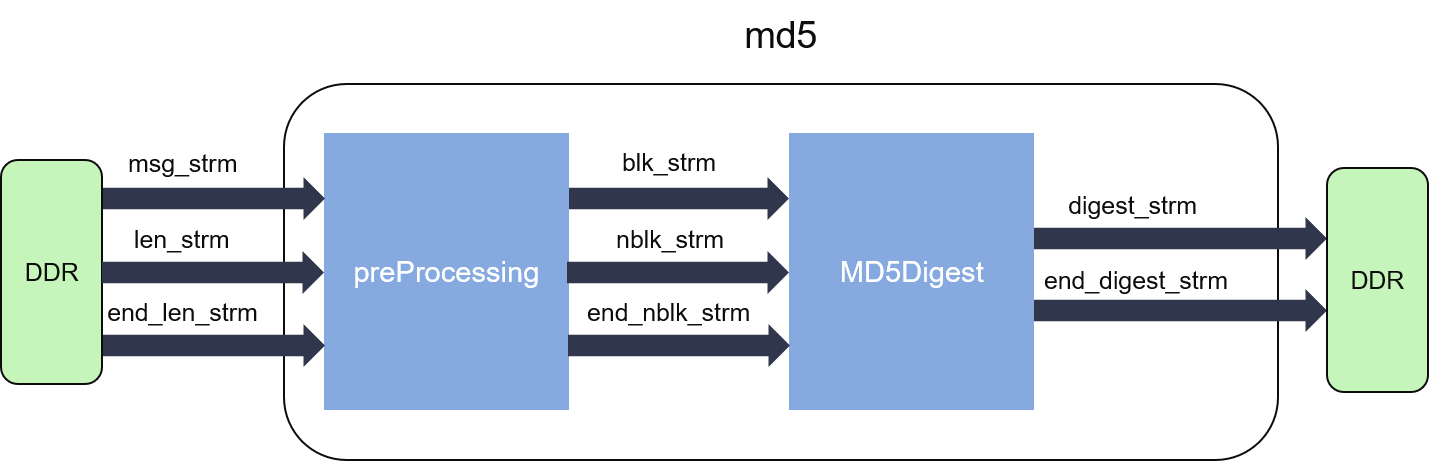
As we can see from the figures, the hash calculation can be partitioned into two parts.
- The pre-processing part pads or splits the input message which is comprised by a stream of 32-bit words into fixed sized blocks (512-bit for each).
- The digest part iteratively computes the hash values. Loop-carried dependency is enforced by the algorithm itself, thus this part cannot reach an initiation interval (II) = 1.
As these two parts can work independently, they are designed into parallel dataflow processes, connected by streams (FIFOs).