SHA-1 Algorithm¶
Overview¶
The SHA-1 secure hash algorithm is a hash-based cryptographic function, it takes a message of arbitrary length as its input, produces a 160-bit digest. It has a padding and appending process before digest the message of arbitrary length.
The SHA-1 algorithm is defined in FIPS 180.
Implementation on FPGA¶
The internal structure of SHA-1 is shown in the figure below:
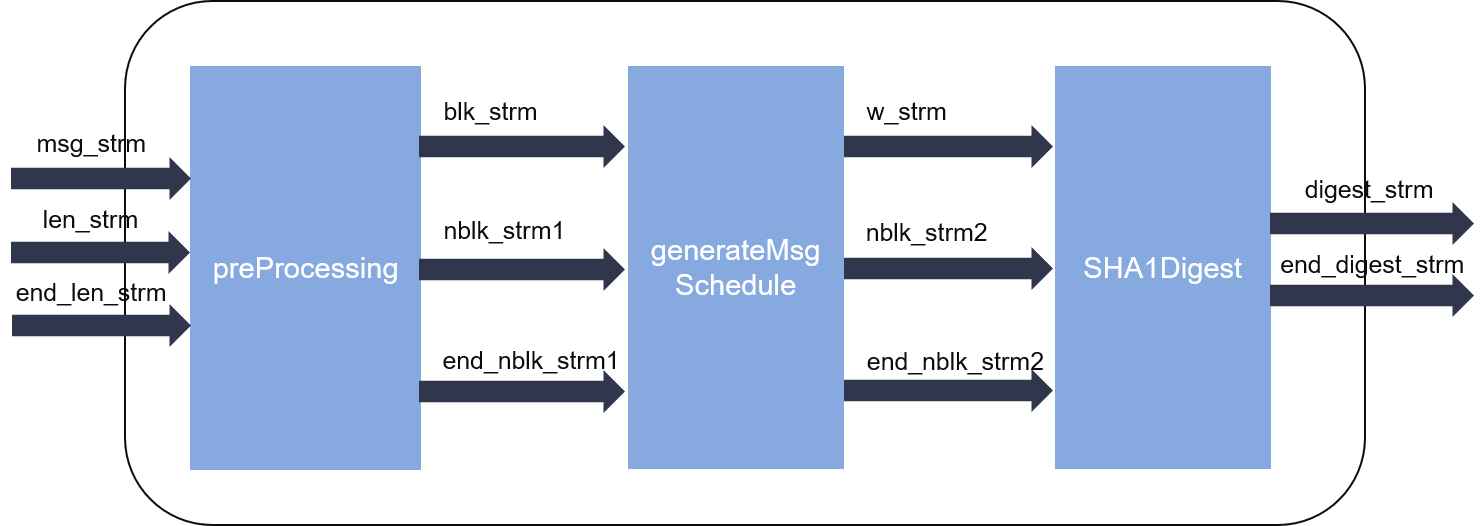
As we can see from the figures, the hash calculation can be partitioned into two parts.
- The pre-processing part pads or splits the input message which is comprised by a stream of 32-bit words into fixed sized blocks (512-bit for each).
- The digest part iteratively computes the hash values. Loop-carried dependency is enforced by the algorithm itself, thus this part cannot reach an initiation interval (II) = 1.
As the two parts can work independently, they are designed into parallel dataflow process, connected by streams (FIFOs).
Performance¶
A single instance of SHA-1 function processes input message at the rate of 512 bit / 84 cycles at 346.62MHz.
The hardware resource utilizations are listed in tab1SHA1 below:
| BRAM | DSP | FF | LUT | CLB | SRL | clock period(ns) |
| 1 | 0 | 7518 | 3633 | 976 | 0 | 3.004 |