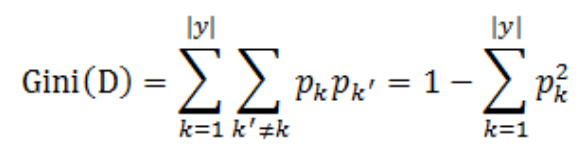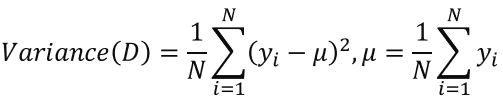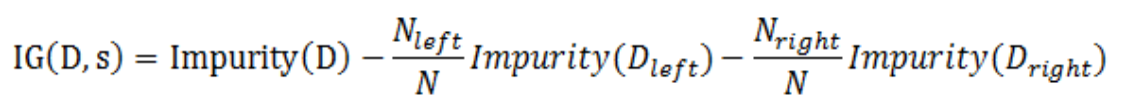Decision Tree (training)¶
Overview¶
Decision Tree (Classification/Regression) is a model to predict sample’s classification or regression value. In structures of Decision Tree, leaf nodes give class labels and internal nodes represent certain attributes. Decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm, divided into two stages of training and inference. In training stage, Eeach partition is chosen greedily by selecting the best split from a set of possible splits, in order to maximize the information gain at a tree node. In inference stage, a decision tree can clearly express the decision process, that is, after series of attributes testing, a sample finally reaches a leaf node.
Basic algorithm¶
Starting from the root node, compute all information gains of all features’ splits to select the best partition as the judging conditions. Following above rules to grow tree nodes, until reach stopping rules:
a.The node depth is equal to the maxDepth training parameter. b.No split candidate leads to an information gain greater than minInfoGain. c.No split candidate produces child nodes which each have at least minInstancesPerNode training instances.
Node impurity and information gain: The node impurity is a measure of the homogeneity of the labels at the node. The information gain is the difference between the parent node impurity and the weighted sum of the two child node impurities. We use gini impurity and variance impurity for classification and regression scenario espectively. Meanwhile, information gain is used to find the best feature split in our implementation.
Caution
Current implementation provides one impurity measure (gini) for classification, and one impurity (variance) for regression. Entropy (only for regression) is to be extended.
Implementation¶
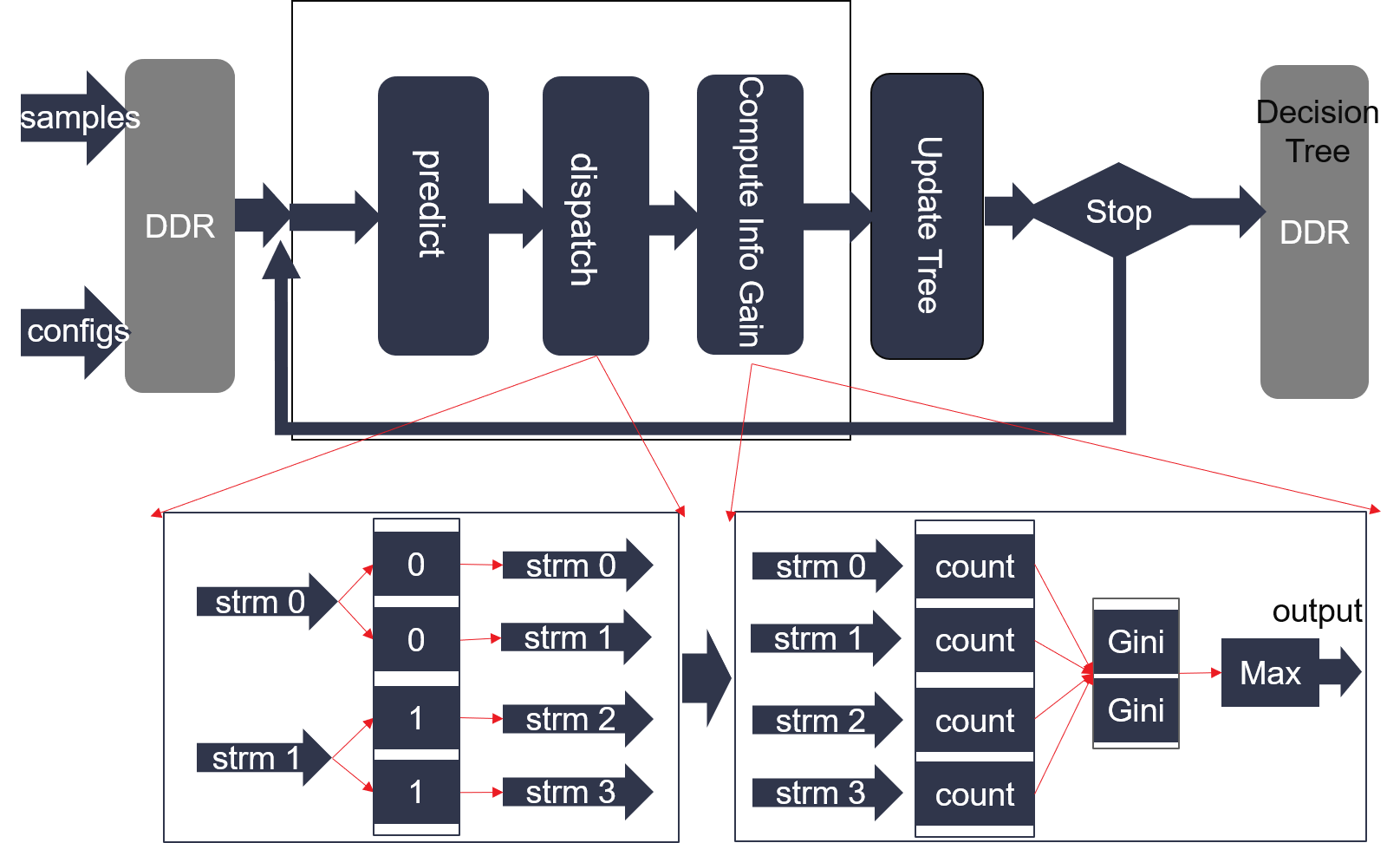
The decision tree training engine (for both classfication and regression) is shown in the figure below:
As we can see from Figure 1, decision tree training engine is an iteration processing, in which one round has three main modules:Predict, dispatch, CIG(Compute Info Gain), and UpdateTree. Stop conditions of decision tree training engine includes: Max depth of Decision Tree, Min instance number in Per Node and Min Info Gain. In one training round, Predict, dispatch and CIG are located in dataflow region. Samples, parameters and final decision tree are saved in 512-bit width DDR arrays. Predict module uses same design method of Decision Tree Predicting in L1, this module is used to predict which node a sample locates in, if the node is not in current tree layer, the sample will be discard.
Detailed implementations can be found at the bottom of Figure 2, dispatch module inputs raw sample streams, and outputs a fixed number of streams. Number of output streams are same with the array length in the middle of dispatch detailed module. Suppose the \(i-th\) element in the dispatching array is \(n\), data of \(i-th\) output stream will come from \(n-th\) input stream.
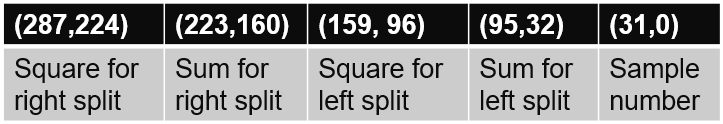
In CIG module of decision tree classification, statistic count and Gini are main parallel design. Count module takes corresponding input and judges if make a adder operation on its URAM elements. Then, each URAM array is read by Gini Unit to compute info gain. Finally, all the info gains are merged to compute the max one and output into UpdateTree module. For regression, the layout of URAM array is like that in classification implementation. The depth of each URAM element is changed to max_parallel_node_num * 9, and the data width of each URAM is 288bits which can be breakdown in the Figure 3.
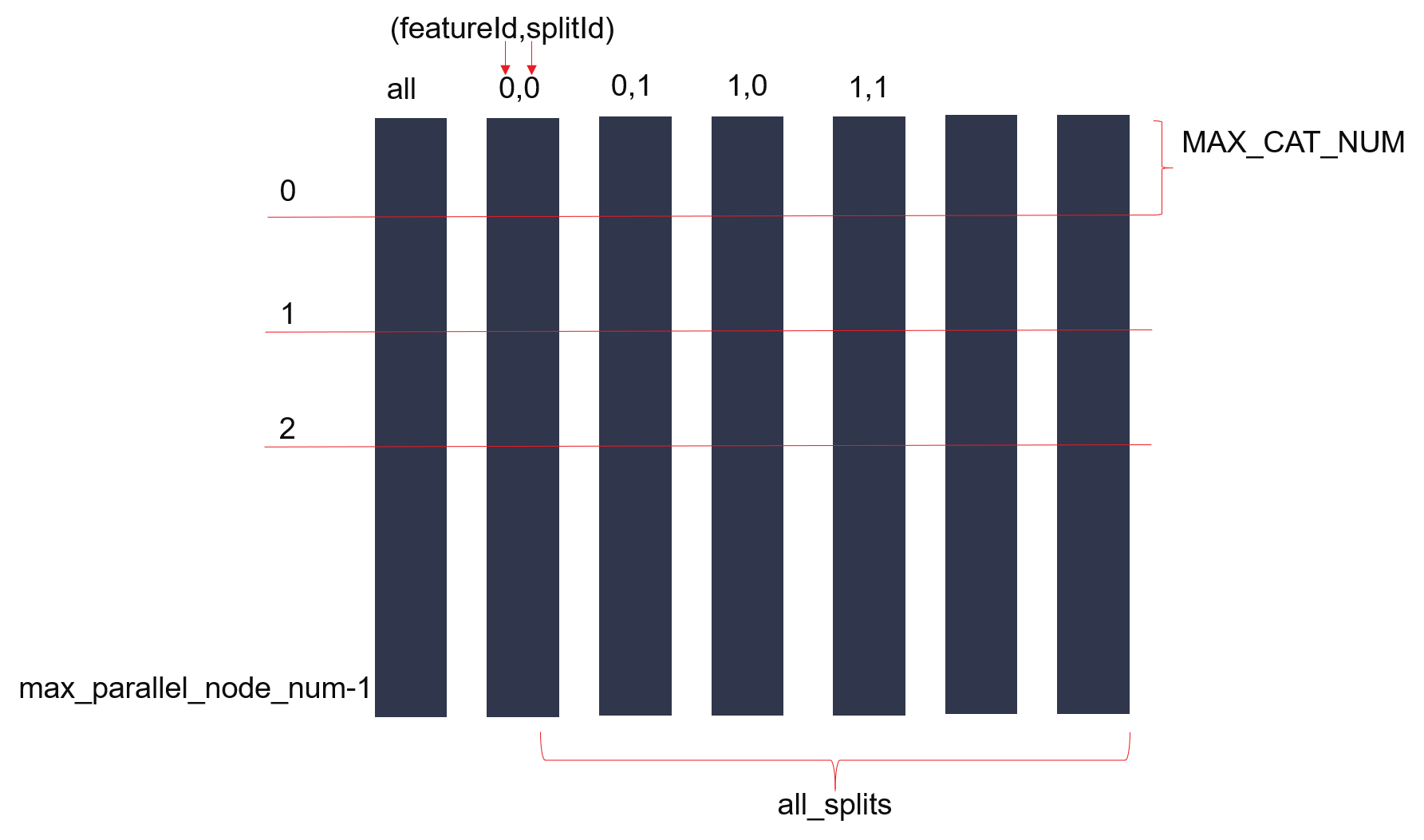
Figure 2 shows the parallel designing using URAM.
There are \(max_split_num\) URAM, so sum of all the feature splits will be limited by this value. Only for regression, an extra \(max_split_para\) parameter is used to control the number of feature split in parallel. As a result, it requires \((split_num+max_split_para-1)/max_split_para\) rounds of iteration to find the best candidate feature spilt for each node. Each count maintains a URAM array, the URAM arrays store all the \(max_parallel_node_num\) statistic info for computing info gain. In training processing, Suppose node number of current tree layer is \(N\), after \((N+max_parallel_node_num-1)/max_parallel_node_num\) rounds of iteration, all the nodes in current layer complete splitting.
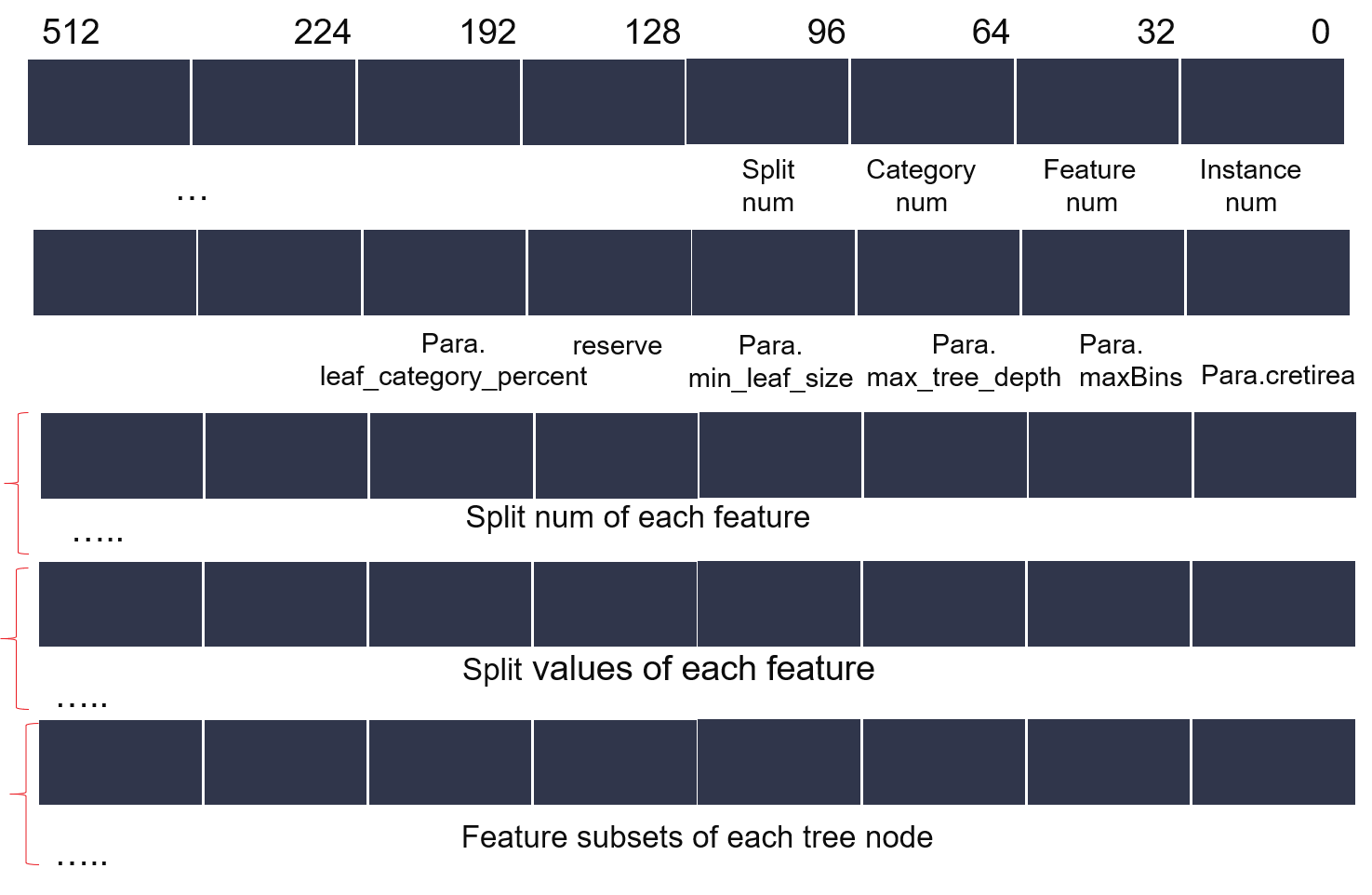
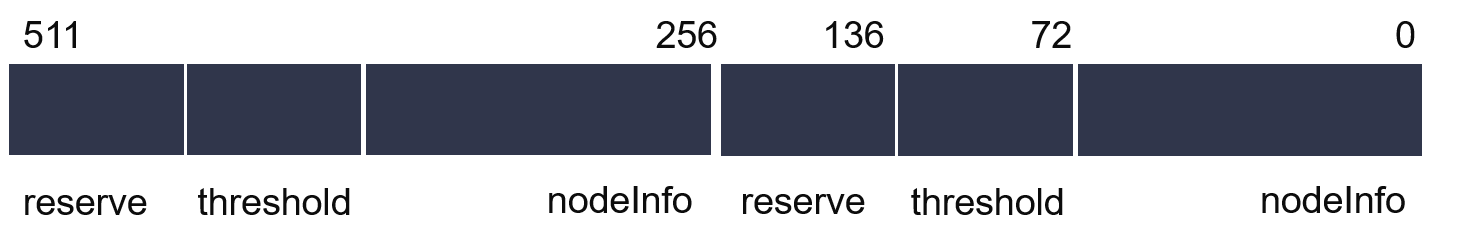
In decision tree function, the first row of data array (ddr buffer) is reserved. From the second row, instances are closely arranged in rows.Figure 4~5 shows the config and tree layout of decision tree.
Caution
Current decisiontree limitations: max feature num is 64, max total split num of all feautures is 128, max tree node in each tree is 4096.
Resource Utilization¶
The decision tree is validated on Alveo U250 card. The hardware resources utilization of two kernels are listed in the table above with its own configuration. This is for the demonstration as configured by default (one engine in one slr). The number of engines in a build may be configured by the user.
| Name | LUT | LUTAsMem | REG | BRAM | URAM | DSP |
|
247,310 | 67,037 | 316,694 | 202 | 173 | 31 |
| 57.25% | 33.90% | 36.65% | 29.99% | 54.06% | 1.01% | |
| DecisionRegression (16x448 at 228MHz) | 243,202 | 46,005 | 274,056 | 210 | 110 | 154 |
| 56.30% | 23.26% | 31.72% | 31.25% | 34.38% | 5.01% |