CSV Parser¶
Comma-separated values file is a popular format which simplily delimited values by commas. CSV parser aims to accelerate explaining each input row with user-defined schema. And then a standard object-stream is used to egress all the row value of the specified columns.
Features¶
Currently, CSV parser supports the following 6 data type: bool, integer, string, float, double and date. This parser don’t support data type inference, so user should give the right setting for each column in the input schema defination.
For the input CSV file, adjacent fields must be separated by a single comma (Other delimiter is not supported). And any field can be quoted. Note that, the nested comma must be quoted and the embedded double-quote characters and line breaks does not being supported so far. Also, the leading and trailing spaces between fields, as well as the heading record is forbidden.
For output data, CSV parser will allow user to select some columns and only the selected columns would be output by the object-stream interface.
Overall Structure¶
CSV parser is implemented as multiple PU architecture to provide high throughput. The diagram is illustrated as below.
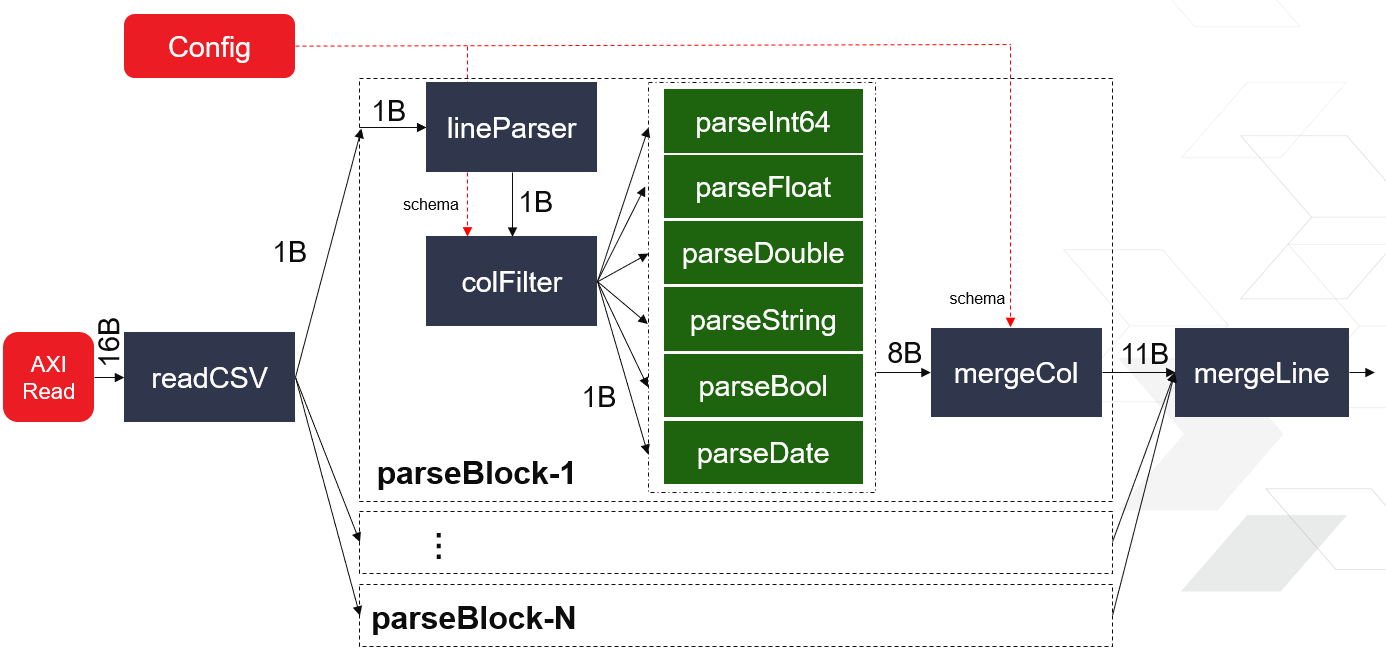
The full CSV file should be loaded in a compacted buffer firstly. For the parallel execution of each PU, the read block will divide the input file into several chunks by its size. Line parser is a FSM-based module to parse out each field at one byte per cycle. Also, all the trivial characters will be removed in this stage. For each data type input, there is one dedicated parse-unit to translate the raw bytes into its own value. At the final stage, each selected field will be merged into one full column before structuring into the output object-stream protocal.