Multinomial Naive Bayes¶
Overview¶
In machine learning, naive Bayes classifiers are a family of simple “probabilistic classifiers” based on applying Bayes’ theorem with strong (naive) independence assumptions between the features. (from wikipedia) Multinomial naive bayes is one of classic naive bayes variants mostly used in document classfication. Each sample represents by the feature vector in which certain events have been counted in multinomial model.
The two parts of multinomial navie bayes algorithm including training and prediction is given as below:
1. Training Stage: count the number of times word term or feature appears across all the training samples, Nyi. And also the number of distinct features in all sample as well as the total number of all features Nyin certain class is counted, respectively. The maximum likelihood probability is the ratio of Nyito Ny, which is one matrix. The prior probability is the ratio of the number of each class to the total number of sample, which is one vector. Additive Laplace smoothing would be used in real applicaton for features not present in the training sample so that zero probabilities can be prevented in the furture classfilier.
- Prediction Stage: for each test sample, the argmax function of the likelihood probability matrix multiply by its feature vector as well as the prior probability vector will get its classification result. And the matrix multiplication can be transformed into matrix addition by the logarithm pre-process.
Implemention¶
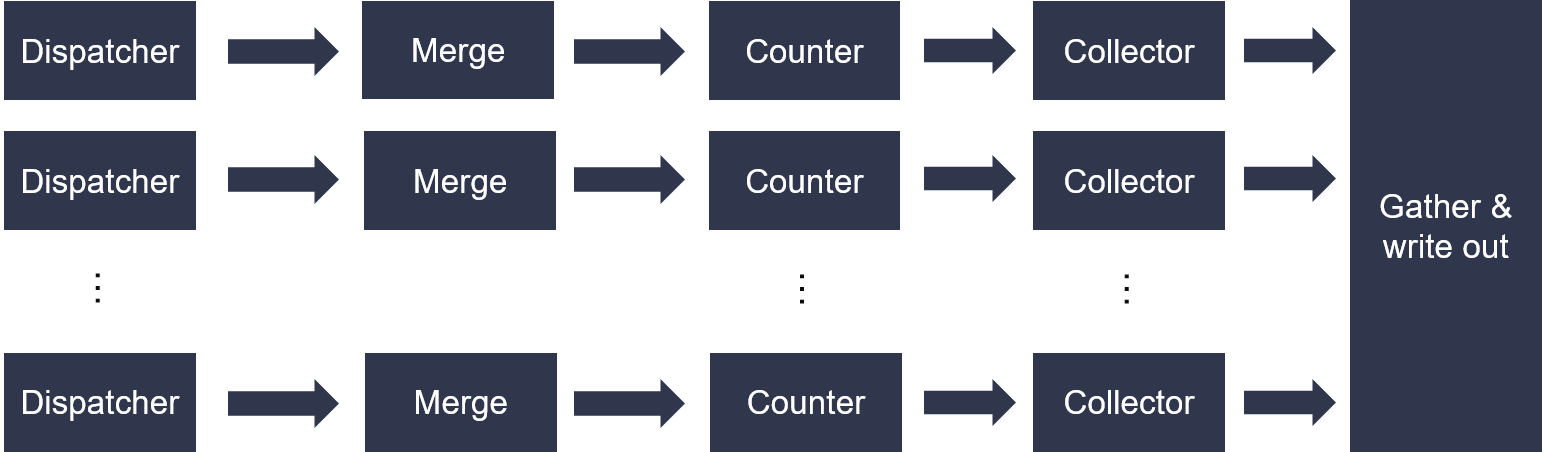
The naive bayes training is one general primitive to acclerate multinomial naive bayes utilizing the advantage of high bandwidth in Xilinx FPGA.
The top diagram is shown as below. Workload is distributed based on LSBs of feature value of one sample to processing data path, so that each path can work independently.
The dispatcher and merge module is feed by compact data format in 64-bit stream. Each 64-bit can be compounded of 12-bit class (from 0), 20-bit feature (from 1) and 32-bit count value. And the input feature vector can be sparse or dense. The end -1 of each sample must be tagged in 20-bit feature slot.
The counter module is responsible for counting the number of times feature appears across all the sample. And the collect module will count the number of all feature for certain class. All statictis result in each data-path will be gather in the following module. Finally, the logarithm result of likelihood and prior probability will be streamed out, respectively.
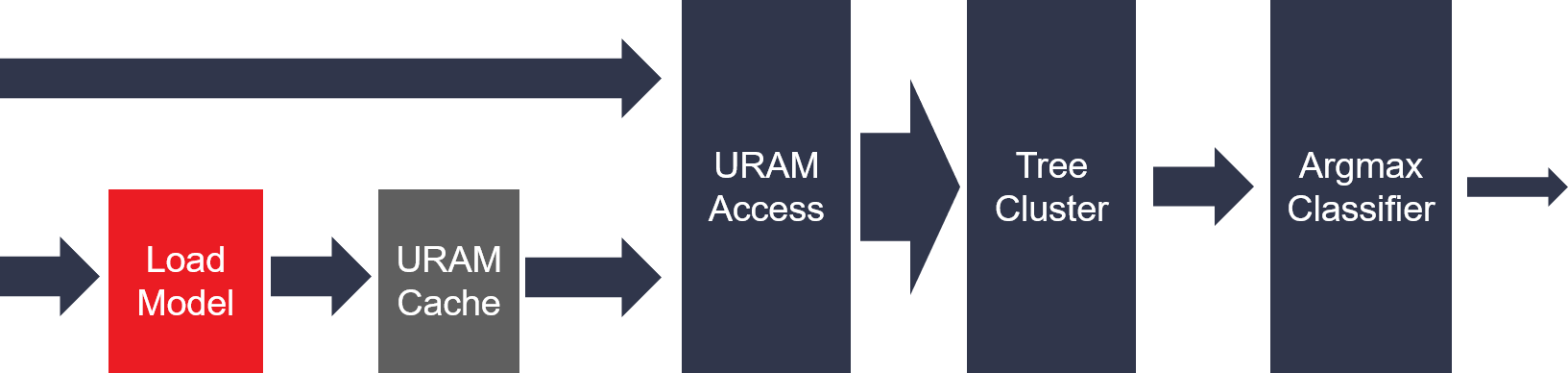
The following figure has been shown as the top structure of naive bayes classfiler. The training model will stream in firstly before the actual prediction process. The whole training model will be cached on on-chip memory. Only the 32-bit count value in test sample would be streamed into the classfiler primitive. And only dense feature vector is supported. The matrix multiplication would be handled in the tree cluster module. The argmax module would predict the result for each sample.
Resource Utilization¶
The hardware resource utilization of naive bayes training (8 channels) and predict (4 data-path and 8 channels) primitive is shown in the table below (synthsis at 300MHz).
| Primitive | LUT | Register | BRAM | URAM | DSP |
| Train | 71553 | 77280 | 190 | 256 | 469 |
| Predict | 75234 | 70702 | 64 | 256 | 411 |
Benchmark Result on Board¶
Meanwhile, benchmark results at 267MHz frequency on Alveo U200 board with 2019.2 shell are shown as below:
| Dataset | samples | classes | features | Spark (4 threads) | Spark (8 threads) | Spark (16 threads) | Spark (32 threads) | Spark (56 threads) | FPGA (:ms) |
| RCV1 | 697614 | 2 | 47236 | 6937 (18.6X) | 7751 (26.2X) | 5636 (12.6X) | 6500 (22.0X) | 5425 (12.2X) | 371 |
| webspam | 350000 | 2 | 254 | 4676 (21.9X) | 5823 (22.6X) | 6869 (40.4X) | 5381 (20.1X) | 5848 (35.3X) | 214 |
| news20 | 19928 | 20 | 62061 | 4249 (361X) | 4728 (453X) | 4256 (319X) | 4388 (332X) | 4308 (391X) | 12 |
Attention
For the training primitive, some padding-zero 64-bit data would be added into the input multi-channel data stream when the total length of feature vector
for all sample cannot be divided evenly by 8 including the ending -1 tag. And the multiplication of the number of class and feature cannot be greater than
2 million so far.
For the predict primitive, the sampe padding-zero 32-bit data would also be added when the length of feature vector for each sample cannot be divided evenly
by the number of channel. And the multiplication of the number of class and feature cannot be greater than 1 million.