STRTree Engine¶
Overview¶
STRTree (Sort-Tile-Recursive Tree) Engine is an GeoSpatial index engine that uses bottom-up way to build an R tree for two-dimensional points. The STR tree packed R tree is simple to implement and maximizes space utilization; that is, as many leaves as possible are filled to capacity. Overlap between nodes is far less than in a basic R-tree. However, once the tree has been built, points cannot be added or removed.
Algorithm¶
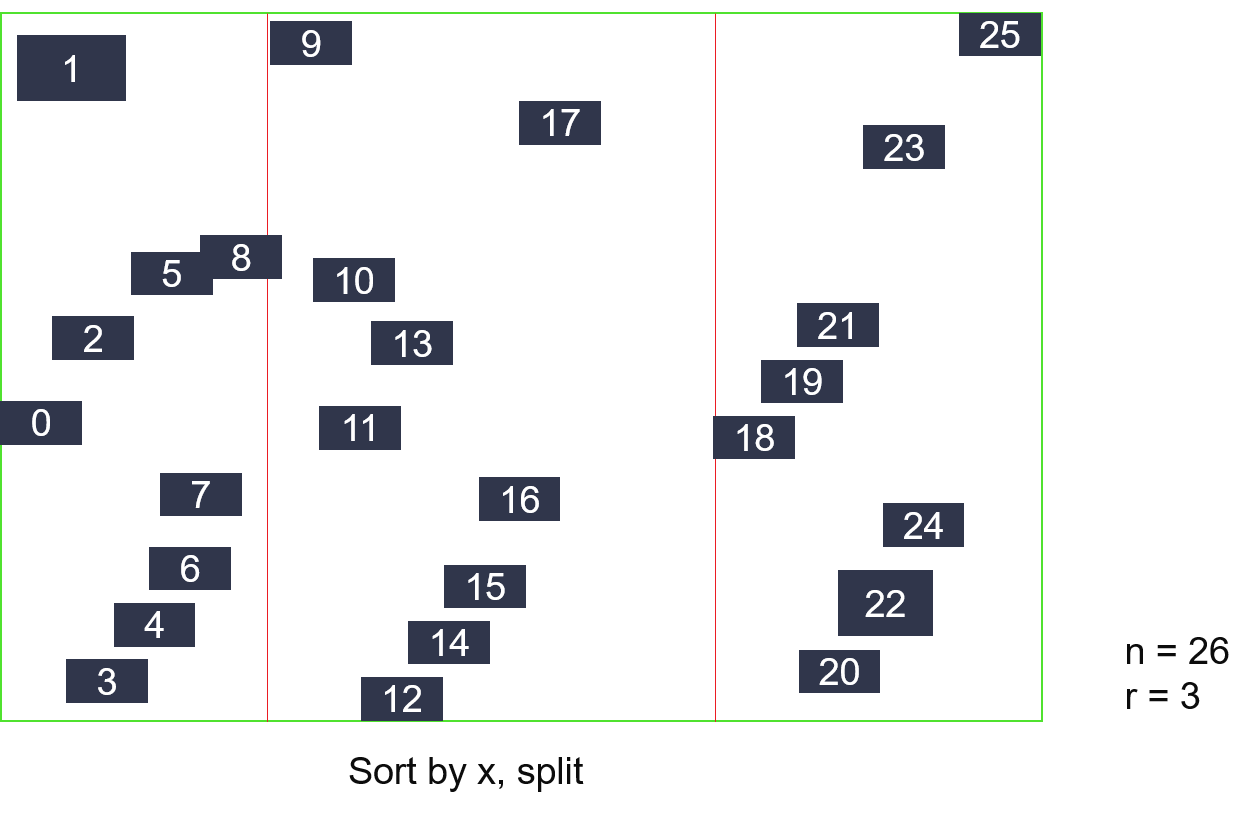
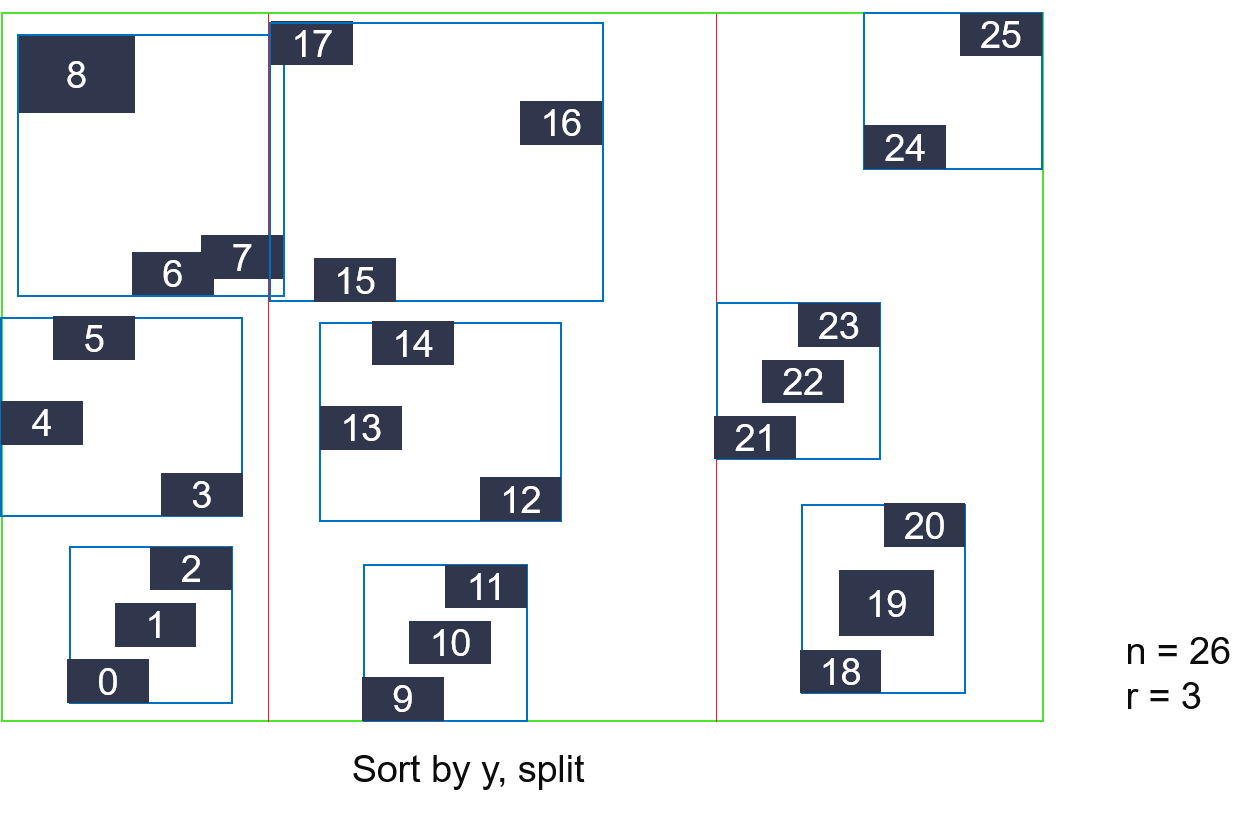
There are n nodes (rectangles), and the center point of its i-th node is represented as (xi, yi). A parent node has at most r child nodes.
- Sort all nodes according to x.
- Divide all nodes into sqrt (n/r) parts, each of which is sorted by y.
- Every r nodes are merged into a new parent node.
- Repeat (1)~(3) until the number of parent nodes is 1.
Implementation¶
STRTree Kernel is implemented according to the algorithm flow. Its core design is the sorting of a dataset (x, y, id). In order to realize the sorting of data (size>16M+), two sorting modules are provided here: blockSort and mergeTreeSort.
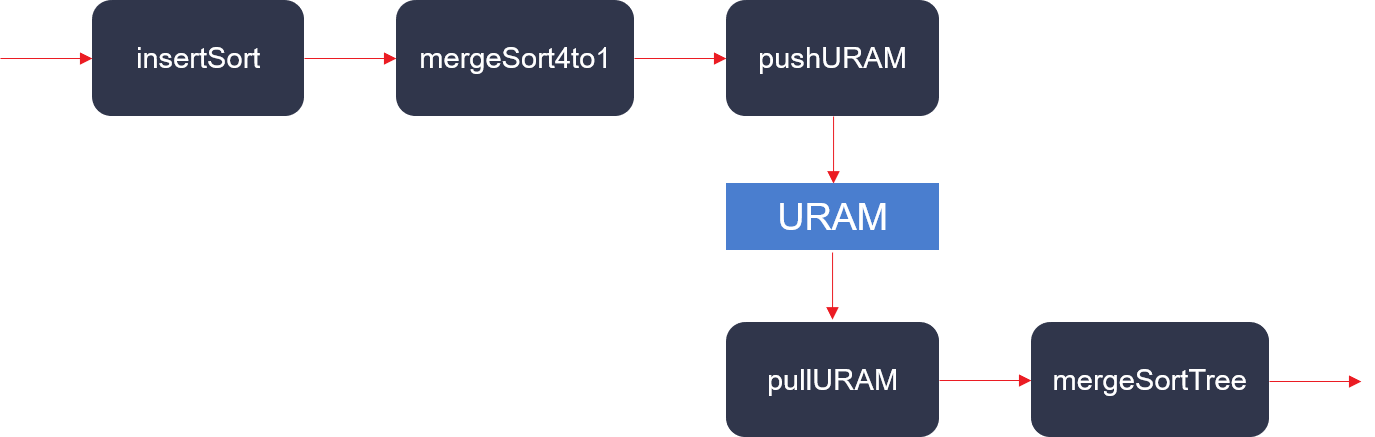
blockSort¶
For input data (size = N), it divides the data into M blocks, sorts each block, and obtains M ordered blocks. The size of N depends on the capacity of the DDR, and the size of M depends on the in-chip LUT and URAM resources. Its design is show in the figure below:
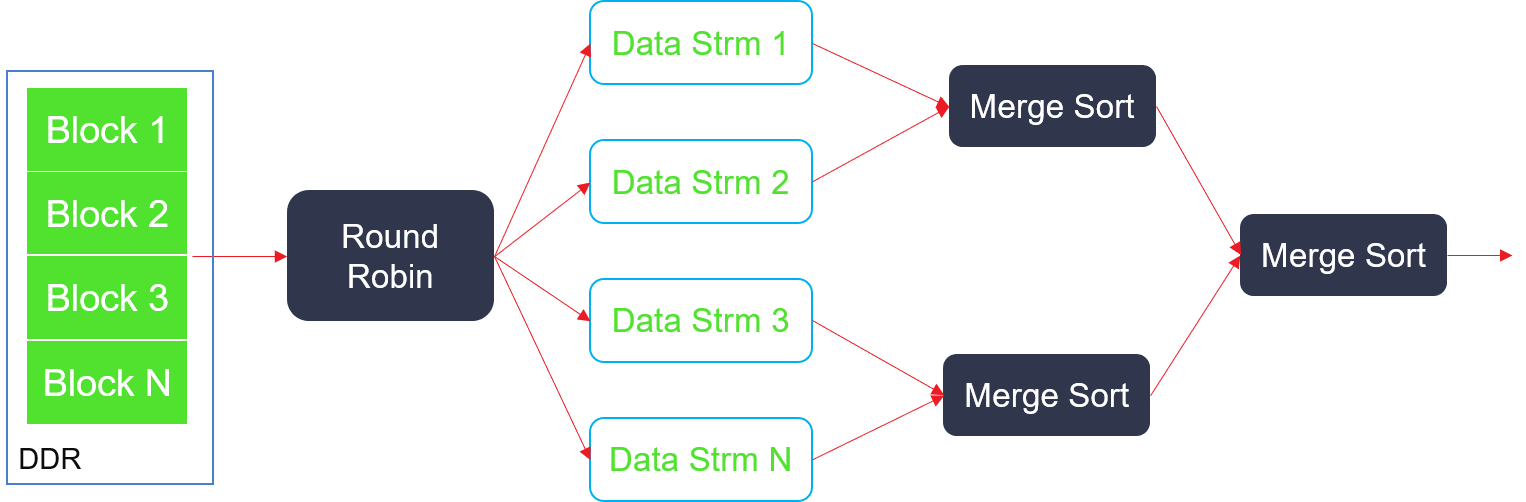
mergeTreeSort¶
For K ordered blocks as input, it can get all data ordered output. The size of K cannot affect the frequency of the kernel, and it can also ensure that each cycle outputs a data. ts design is show in the figure below:
Resource Utilization¶
The Kernel is validated on Alveo U200 card. The hardware resources utilization are listed in the table above (not include Platform).
| Name | LUT | REG | BRAM | URAM | DSP | Freq |
|
148,278 | 159,273 | 30 | 324 | 22 | 183 MHz |
| 12.54% | 8.36% | 1.39% | 40.50% | 0.32% |