RTM Kernels¶
RTM kernels are used to realize the forward and backward wave propagation paths. They are constructed by connecting multiple forward (see: Forward streaming module) and / or backward (see: Backward streaming module) modules and data mover modules together. The RTM applications in this library is realized on Xilinx Alveo U280 card, which has 2 HBM stacks and 2 DDR device modules attached to the FPGA. Each HBM stack stores 4GB data, 8GB storage in total. Each DDR device stores 16GB data, 32GB storage in total. The RTM kernels use HBM devices to store the wavefield data, image data and velocity model data. The boundary values and other parameters including the source and receiver data are stored in DDR devices.
2D-RTM forward kernel¶
As shown in Figure 1, several parallel running forward streaming modules are connected via FIFOs
to compute several wavefield time steps simultaneously. The number of connected forward streaming
modules is configurable at compile time, and decides the freqency of device memory access for retriveing data.
For example, if 10 forward streaming modules are connected, that means the data retrieved form each device memory access
can sustain the computation of 10 wavefield time steps. The C++ implementation of 2D-RTM forward kernel can be found in
L2/include/hw/rtm2d/rtmforward.hpp.
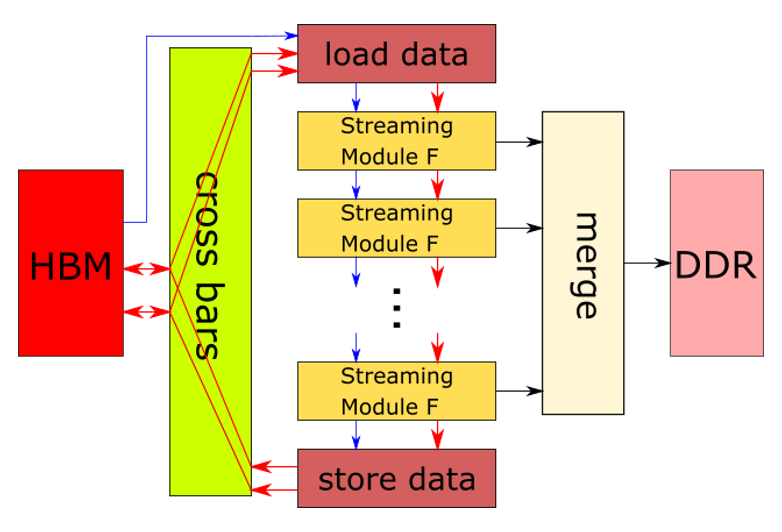
Figure 1. 2D-RTM forward kernel
2D-RTM backward kernel¶
As shown in Figure 2, several backward streaming modules are connected via FIFOs to compute multiple wavefield time stpes and corelate the image at the same time. The number of connected backward streaming modules be configured at compile time. The C++ implementation of 2D-RTM backward kernel can be found in L2/include/hw/rtm2d/rtmbackward.hpp.
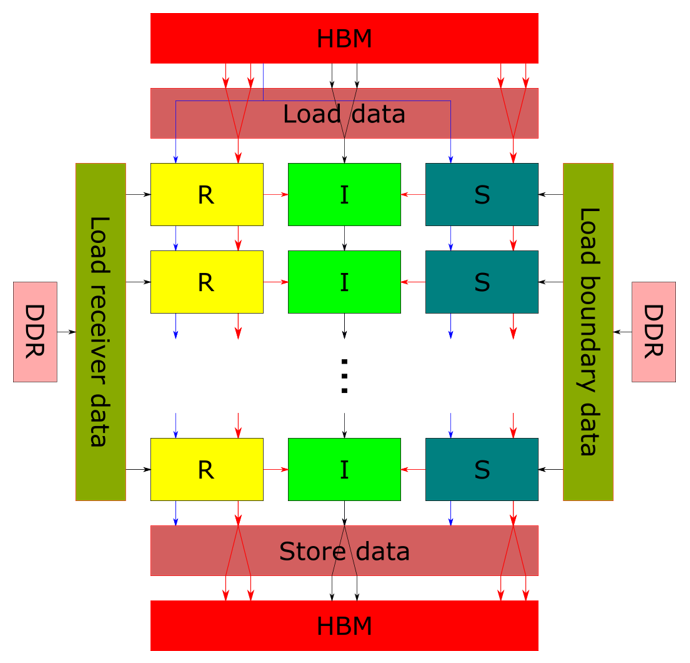
Figure 2. 2D-RTM backward kernel
3D-RTM forward kernel¶
3D-RTM forward kerenl has similar hardware architecture with the 2D-RTM forward
kernel.
There are two types of forward kernel with two different boundary
condition, HBC (hybrid boundary condition) and RBC
(random boundary condition).
The C++ implementation of 3D-RTM forward kernels can be found in L2/include/hw/rtm3d/.