Copyright 2019 Xilinx, Inc.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the “License”); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an “AS IS” BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Decision Tree (Predict)¶
Overview¶
Decision Tree (Classification/Regression) is a model to predict the classification or regression value of given samples. In structures of Decision Tree, leaf nodes give class labels and internal nodes represent certain attributes. Decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm, divided into two stages of training and predict. In training stage, each partition is chosen greedily by selecting the best split from a set of possible splits, in order to maximize the information gainat a tree node. In predict stage, a decision tree can clearly express the decision process, that is, after series of attributes testing, a sample finally reaches a leaf node.
Algorithm (predict)¶
Predict stage is the process of making a decision using a decision tree. Starting from the root node, test the corresponding feature attributes in the item, and select the output branch according to its value until it reaches the leaf node. Finally, use the category value or regression value stored by the leaf node as the decision result.
The decision tree can be linearized into decision rules, where the outcome is the contents of the leaf node, and the conditions along the path form a conjunction in the if clause. In general, the rules have the form: if condition1 and condition2 and condition3 then outcome.
Suppose :match:`N` is the number of samples, :match:`Nodes`, an array of special data structure, represents a decision tree.:math:MAX_DEPTH is max depth of decision tree.
The detailed algorithm: Input: a sequence of samples and Decision Tree (marked as \(nodes\)). Output: a sequence of predict results.
- For m from 1 to \(N\)
- For k from 1 to \(MAX_DEPTH\)
- if \(nodes[k]\) is not leaf node
- test corresponding feature attributes and select a branch.
- else
- output the category or regression value of current node. break
Implementation (predict)¶
In decision tree predict, each sample read \(i\) layer to select a branch to \(i+1\) layer. The max loop number of each sample is \(MAX_DEPTH\) Based on the algorithm, the description of decision tree predict if provided by the following figure.
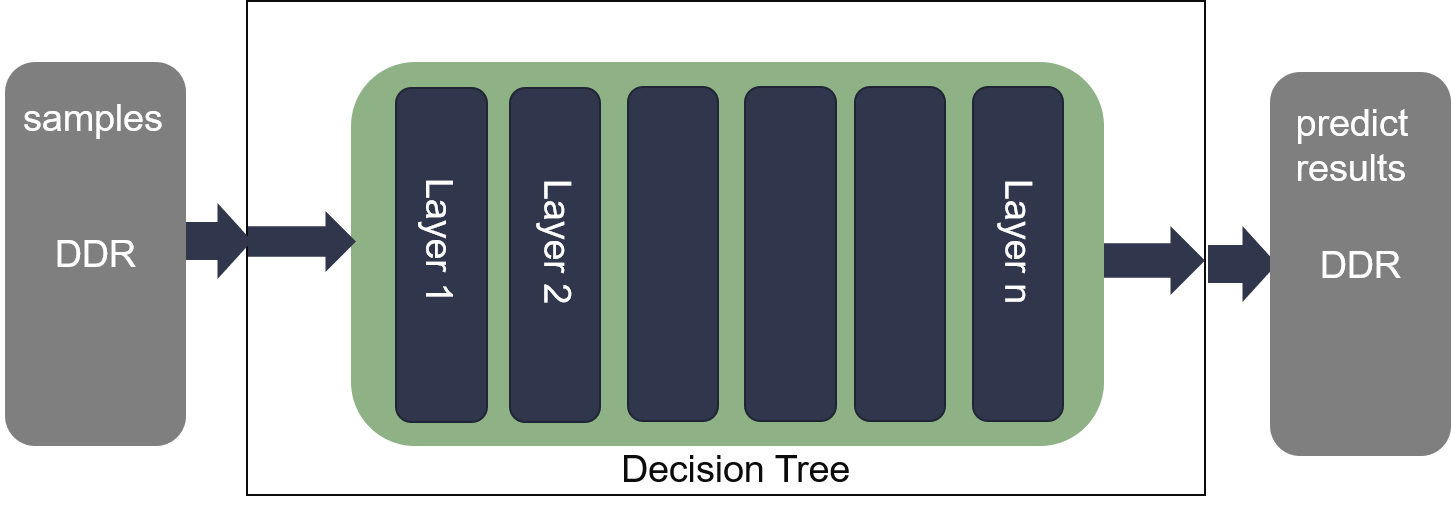
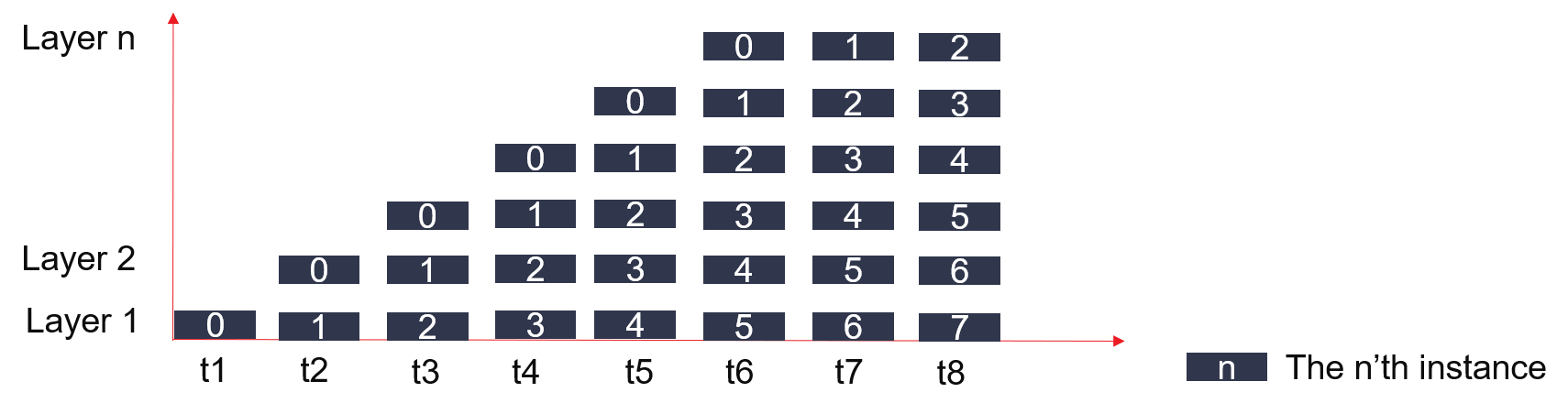
To eliminate the loop-carried dependency for memory port deficiency, we partition different layers of decision tree in differen URAM. In batch mode predict, each sample reads various uram, each round has no dependence so that the initiation interval (II) could achieve to 1. It is present as follows:
Profiling¶
For decision tree classification predict,
The hardware resources for Decision Tree with max tree depth 16:
Engines SRL URAM FF LUT clock period(ns) Decision Tree Predict 61620 17 68681 81673 2.900
The hardware resources for Decision Tree with max tree depth 20:
Engines SRL URAM FF LUT clock period(ns) Decision Tree Predict 78052 21 85734 102923 2.937
For decision tree regression predict,
The hardware resources for Decision Tree with max tree depth 10:
Engines SRL URAM FF LUT clock period(ns) Decision Tree Predict 18504 11 42994 31031 3.844
The correctness of Decision Tree Predict is verified by comparing results with Decision Tree predict results of Spark mllib.