BLAKE2 Algorithms¶
Overview¶
BLAKE2 is a set of cryptographic hash functions defined in RFC 7693: The BLAKE2 Cryptographic Hash and Message Authentication Code (MAC).
The BLAKE2 family consists of 2 hash functions, and both of them provide security superior to SHA-2. The BLAKE2B is optimized for 64-bit platforms, while the BLAKE2S is optimized for 8-bit to 32-bit platforms.
Currently this library supports BLAKE2B algorithm.
Implementation on FPGA¶
The internal structure of BLAKE2B algorithm is shown as the figure below:
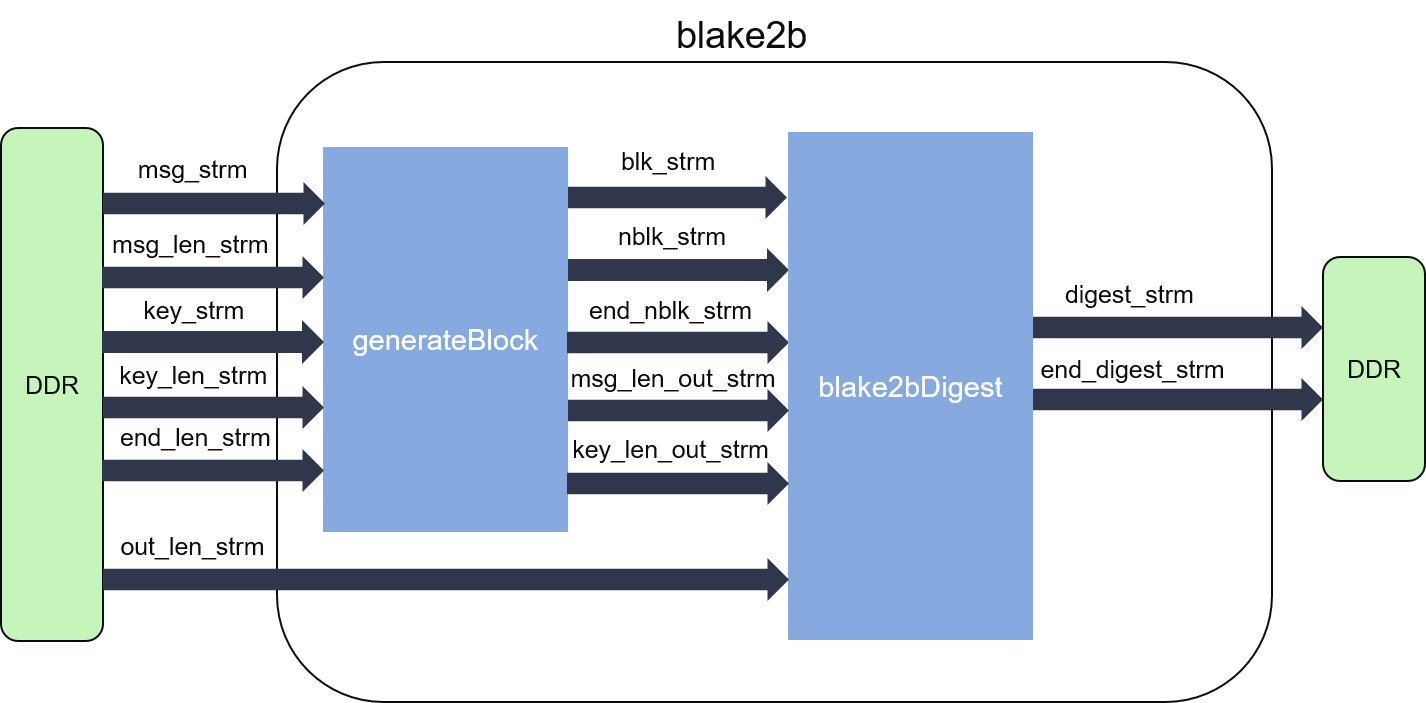
As we can see from the figure, the BLAKE2B hash calculation can be partitioned into two parts.
- The generateBlock module pads the input message and the optional input key into fixed sized blocks, and informs the digest part that how many blocks do we have in this message. The message word size is 64-bit for BLAKE2B, 32-bit for BLAKE2S, and each block has a size of 16 message words.
- The disgest part iteratively computes the hash values. Loop-carried dependency is enforced by the algorithm, and thus this part cannot reach II=1.
As these two parts can work independently, they are designed into parallel dataflow process, connected by streams (FIFOs).
Performance¶
BLAKE2B¶
A single instance of BLAKE2B function processes input message at the rate of
1024 bit / 737 cycles at 315.95MHz.
The hardware resource utilizations of BLAKE2B is listed in tab1BLAKE2B below:
| BRAM | DSP | FF | LUT | CLB | SRL | clock period(ns) |
| 0 | 0 | 20665 | 15635 | 3466 | 0 | 3.053 |