XTS mode¶
Overview¶
The XTS working mode is a typical block cipher mode of operation using block cipher algorithm. The acronym of XTS stands for XEX Tweakable Block Ciphertext Stealing. According to this “ciphertext stealing” method, XTS can encrypt or decrypt sequences of arbitrary length of data block. i.e., data string that is 256 bits or 257 bits. Therefore, in XTS mode, the input or output data may also consist of a number of blocks in 128 bits followed by a separated partial block which is not empty and less than 128 bits. By IEEE Std 1619-2007, two cipherkeys in 256 bits are required in XTS mode. They are called tweakable key and encryption key, respectively.
Implementation on FPGA¶
We support XTS-AES128 and XTS-AES256 modes in this implementation.
Attention
The bit-width of the interfaces we provide is shown as follows:
| plaintext | ciphertext | cipherkey | IV | textlength | |
| CBC-AES128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 64 |
| CBC-AES256 | 128 | 128 | 256 | 128 | 64 |
The algorithm flow chart is shown as follow:
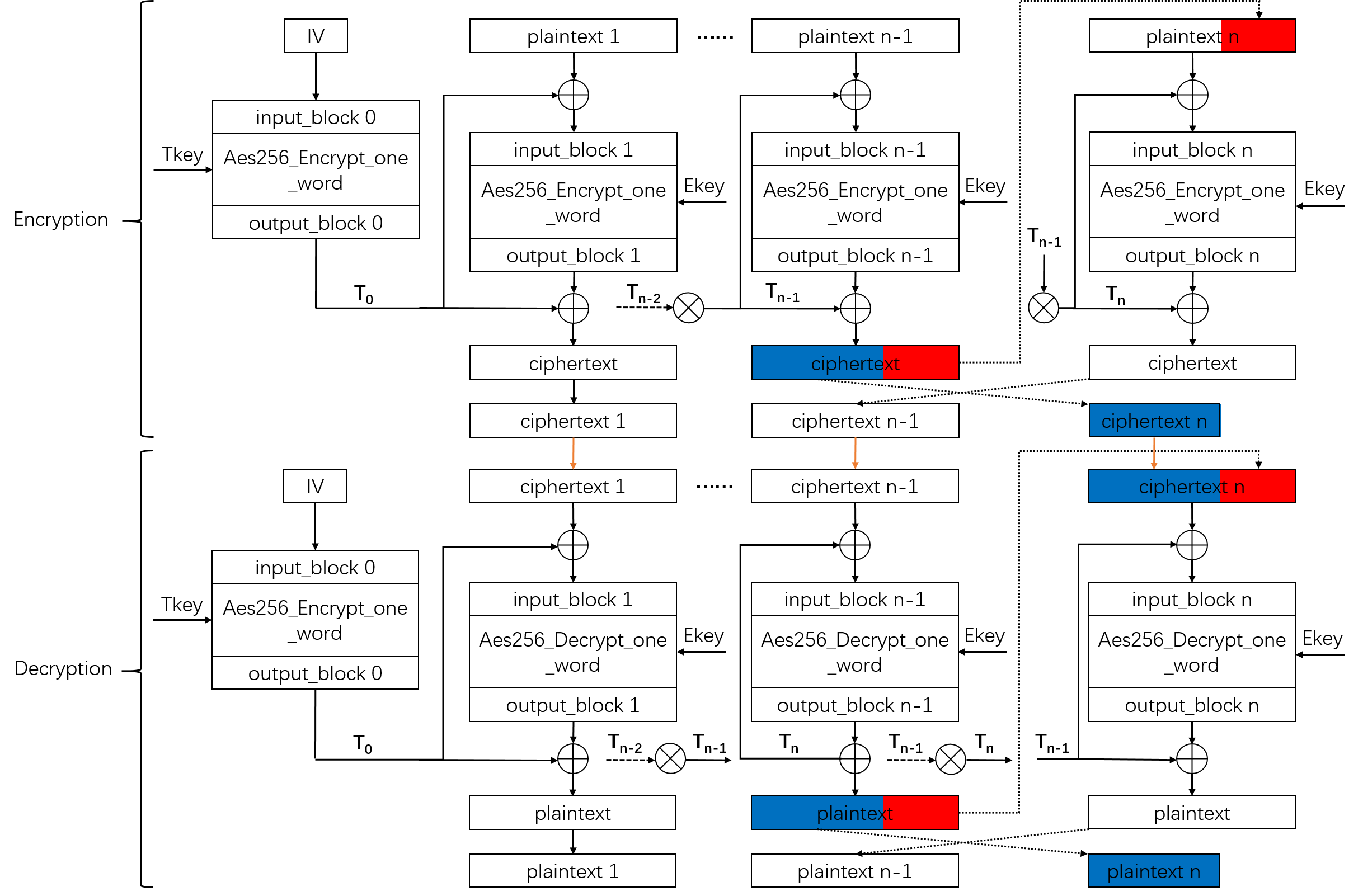
As we can see from the chart, the dependency of XTS encryption flow only exists between the first block and the second to last block. It is same as shown in XTS decryption flow. Therefore, the initiation interval (II) of XTS encryption and decryption mode can achieve 1. Notice that one one-word AES encryption module is instanced in XTS decryption.
Profiling¶
XTS-AES128 encryption¶
| CLB | LUT | FF | DSP | BRAM | SRL | URAM | CP(ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2942 | 15963 | 8329 | 0 | 2 | 643 | 0 | 3.160 |
XTS-AES128 decryption¶
| CLB | LUT | FF | DSP | BRAM | SRL | URAM | CP(ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6557 | 32061 | 15739 | 0 | 12 | 579 | 0 | 3.123 |
XTS-AES256 encryption¶
| CLB | LUT | FF | DSP | BRAM | SRL | URAM | CP(ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4563 | 22474 | 14867 | 0 | 2 | 899 | 0 | 3.151 |
XTS-AES256 decryption¶
| CLB | LUT | FF | DSP | BRAM | SRL | URAM | CP(ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8645 | 44796 | 20718 | 0 | 12 | 835 | 0 | 3.141 |