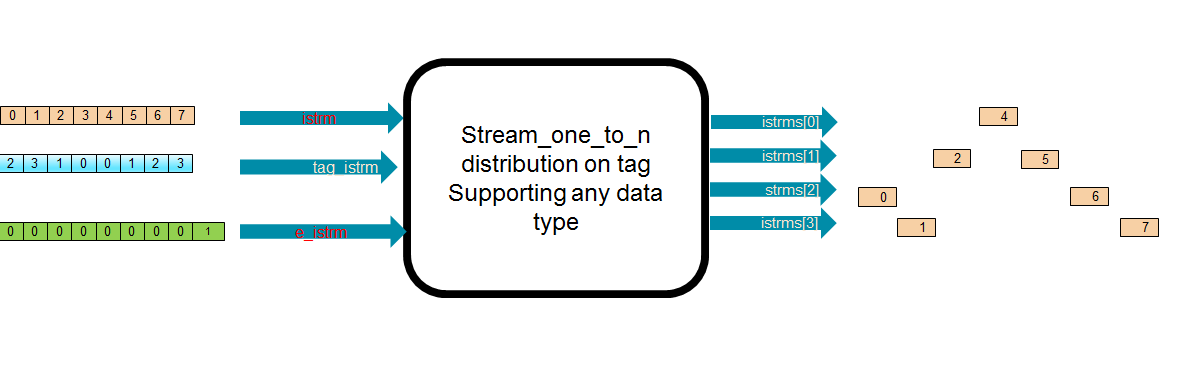
Internals of streamOneToN¶
The streamOneToN API
is designed for distributing data from one source to multiple processor units.
Three different algorithms have been implemented, RoundRobinT,
LoadBalanceT and TagSelectT.
To ensure the throughput, it is very common to pass a vector of elements in
FPGA data paths, so streamOneToN supports element vector input, if the
data elements are passed in the form of ap_uint.
It also offers overload for generic template type for non-vector input.
Round-Robin¶
The round-robin algorithm distributes elements to output streams in circular order, starting from the output stream with index 0.
Generic Type¶
With generic type input, the function dispatches one element per cycle. This mode works best for sharing the multi-cycle processing work across an array of units.
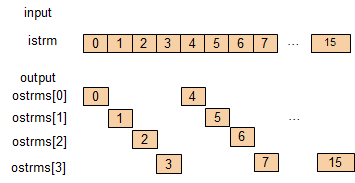
Vector Input¶
With input casted to a long ap_uint vector, higher input rate can be done.
This implementation consists of two dataflow processes working in parallel.
The first one breaks the vector into a ping-pong buffer,
while the second one reads from the buffers and schedules output in
round-robin order.
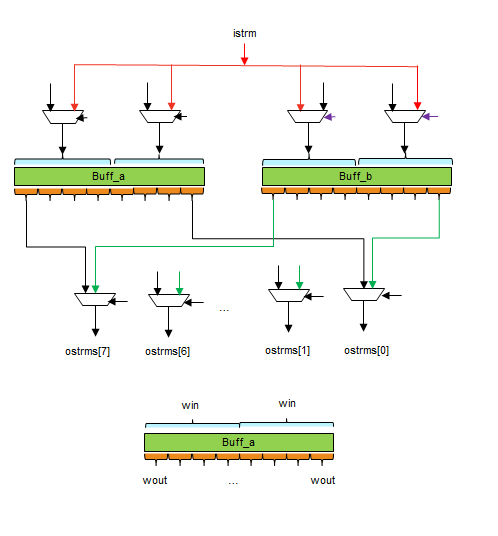
The ping-pong buffers are implemented as two ap_uint of width as least
common multiple (LCM) of input width and total output stream width.
This imposes a limitation, as the LCM should be no more than
AP_INT_MAX_W, which is default to 1024 in HLS.
Caution
Though AP_INT_MAX_W can be set to larger values, it may slow down HLS
synthesis, and to effectively override AP_INT_MAX_W, the macro must be
set before first inclusion of ap_int.h header.
This library tries to override AP_INT_MAX_W to 4096, but it’s only
effective when ap_int.h has not be included before utility library
headers.
Load-Balancing¶
The load-balancing algorithm does not keep a fixed order in dispatching, instead, it skips successors that cannot read, and tries to feed as much as possible to outputs.
Generic Type¶
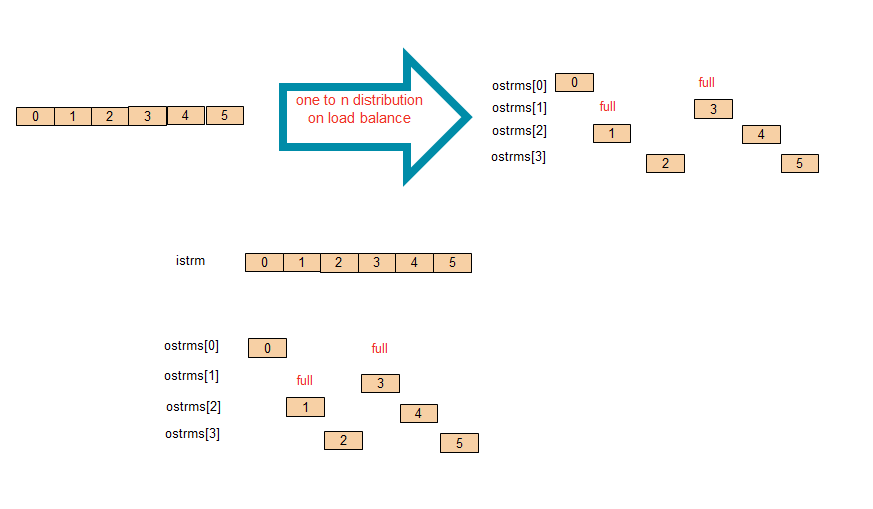
Vector Input¶
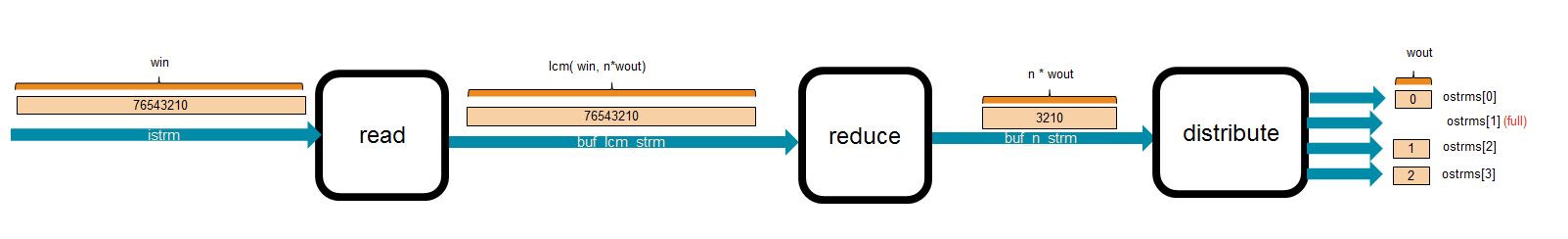
The design of the primitive includes 3 modules:
- read: Read data from the input stream then output data by one stream whose
width is
lcm(Win, N * Wout)bits. Here, the least common multiple ofWinandN * Woutis the inner buffer size in order to solve the different input width and output width. - reduce: split the large width to a array of
Nelements ofWoutbits. - distribute: Read the array of elements, and distibute them to output streams which are not full yet.
Attention
Current implementation has the following limitations:
- It uses a wide
ap_uintas internal buffer. The buffer is as wide as the least common multiple (LCM) of input width and total output width. The width is limited byAP_INT_MAX_W, which defaults to 1024. - This library will try to override
AP_INT_MAX_Wto 4096, but user should ensure thatap_int.hhas not be included before the library headers. - Too large
AP_INT_MAX_Wwill significantly slow down HLS synthesis.
Important
The depth of output streams must be no less than 4 due to internal delay.
Tag-Select¶
This algorithm dispatches data elements according to provided tags. The tags are used as index of output streams, and it is expected that each input element is accompanied by a tag.