Internal Design of PageRankMultiChannels¶
Overview¶
PageRank (PR) is an algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in their search engine results. PageRank is a way of measuring the importance of website pages. PageRank works by counting the number and quality of links to a page to determine a rough estimate of how important the website is. The underlying assumption is that more important websites are likely to receive more links from other websites. Currently, PageRank is not the only algorithm used by Google to order search results, but it is the first algorithm that was used by the companies, and it is the best known.
Algorithm¶
PageRank weighted algorithm implementation:
\(A, B, C ,D...\) are different vertex. \(PR\) is the pagerank value of vertex, \(Out\) represents the out degree of vertex and \(\alpha\) is the damping factor, normally equals to 0.85
The algorithm’s pseudocode is as follows
for each edge (u, v) in graph // calculate du degree
degree(v) += weight(v)
for each node u in graph // initiate DDR
const(u) := (1- alpha) / degree(u)
PR_old(u) := 1.0
while norm(PR_old - PR_new) > tolerance // iterative add
for each vertex u in graph
PR_new(u) := alpha
for each vertex v point to u
PR_new(u) += const(v)*PR_old(v)*weight(v)
sum := 0
for each node u in graph // calculate sum of vector PR
sum += PR_new(u)
for each node u in graph // normalization of order 1
PR_new(u) := PR_new(u) / sum
return PR_new
Implemention¶
The input matrix should ensure that the following conditions hold:
- Directed graph
- No self edges
- No duplicate edges
- Compressed sparse column (CSC) format
- Max 64M Vertex with 128M Edge graph for this design, still board-level scalability.
In order to make the API use higher bandwidth on the board of HBM base, this optimized version for HBM is implemented The algorithm implemention is shown as the figure below:
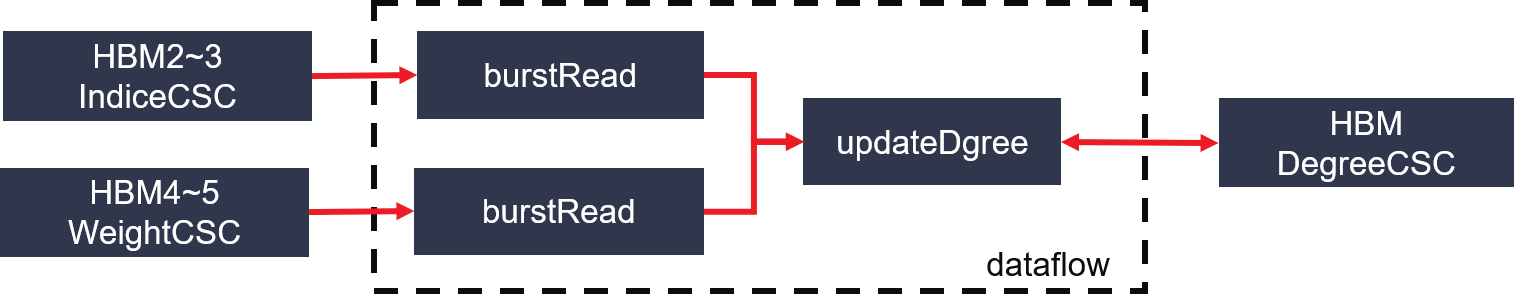
Figure 1 : PageRank calculate degree architecture on FPGA
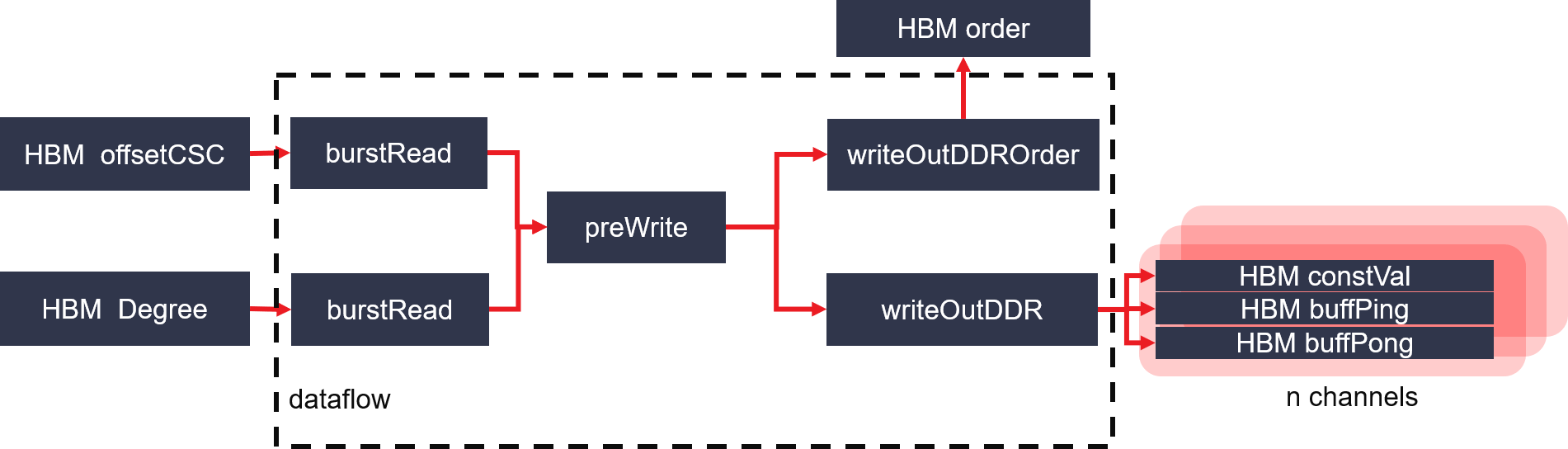
Figure 2 : PageRank initiation module architecture on FPGA
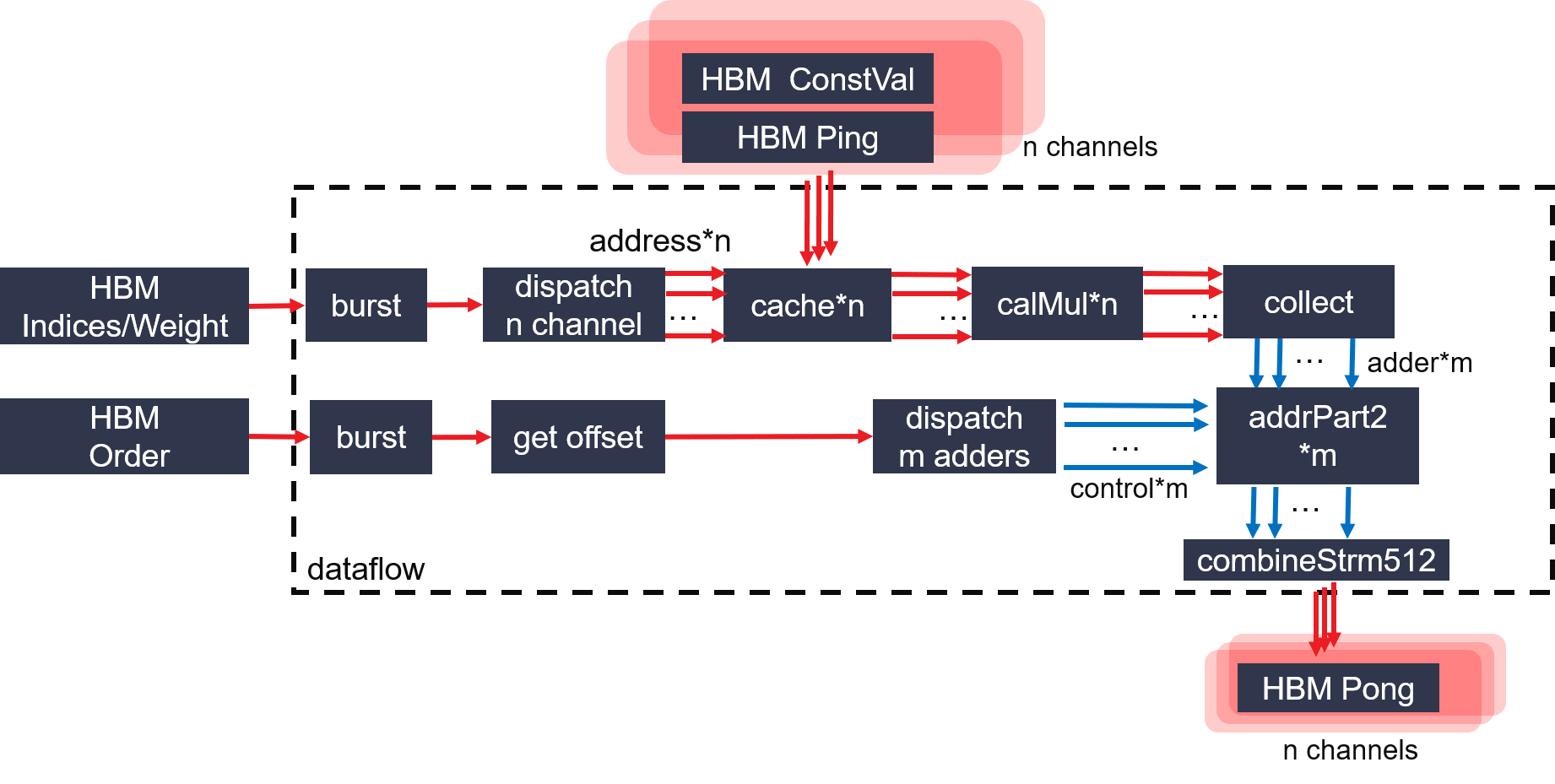
Figure 3 : PageRank Adder architecture on FPGA
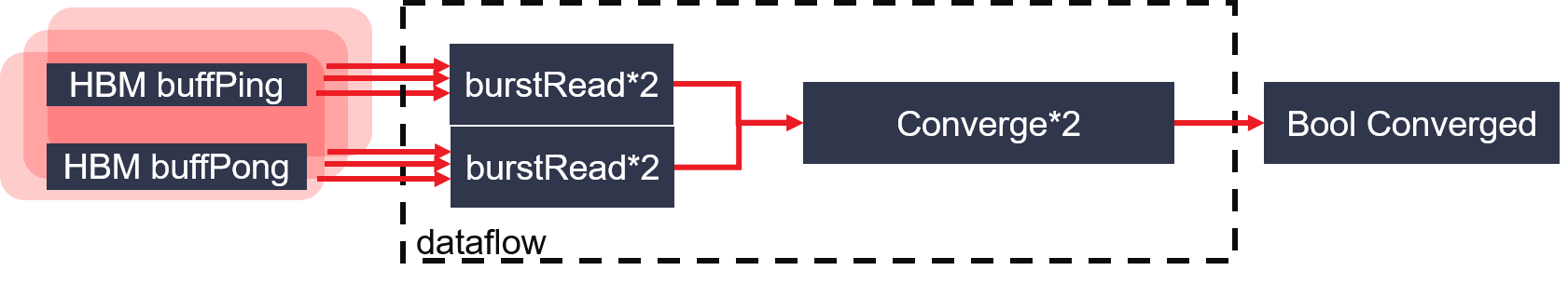
Figure 4 : PageRank calConvergence architecture on FPGA
As we can see from the figure:
- Module calculate degree: first get the vertex node’s outdegree with weighted and keep them in one DDR buffer.
- Module initiation: initiate PR DDR buffers and constant value buffer.
- Module Adder: calculate Sparse matrix multiplification.
- Module calConvergence: calculate convergence of pagerank iteration.
Profiling¶
The hardware resource utilizations are listed in the following table.
Table 1 : Hardware resources for PageRankMultiChannels with 2 channels
| Kernel | BRAM | URAM | DSP | FF | LUT | Frequency(MHz) |
| kernel_pagerank_0 | 425 | 224 | 84 | 352693 | 245636 | 243 |
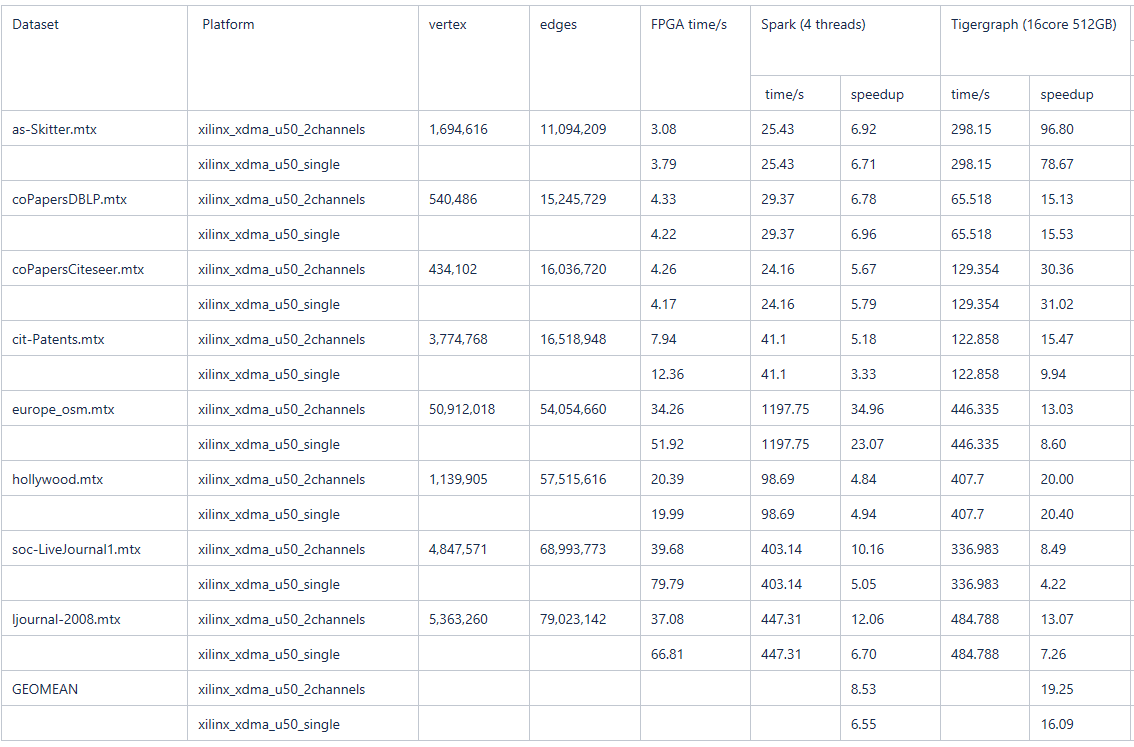
Table 2 : Comparison between CPU tigergraph and FPGA VITIS_GRAPH
Note