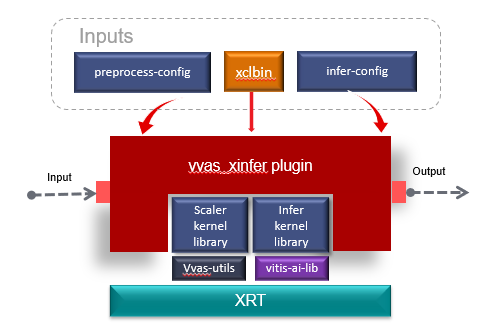
vvas_xinfer¶
The vvas_xinfer GStreamer plug-in is capable of performing inferencing on video frames/images and generating output in the form of a GstInferenceMeta object, which is a tree-like structure containing inference results. This metadata is attached to the input GstBuffer. Additionally, this plug-in can perform hardware-accelerated preprocessing operations, such as resize/crop/normalization, on incoming video frames/images before conducting inferencing. The vvas_xinfer plug-in relies on the Vitis-AI library for inferencing.
The use of preprocessing with the vvas_xinfer plug-in is optional and requires the presence of the image_processing kernel in the hardware design. One can use software image_processing engine too by mentioning in json file. Users may also opt to use software-based preprocessing, which internally uses the Vitis-AI library.
If hardware-accelerated preprocessing is enabled and the vvas_xinfer plug-in is not receiving physically contiguous memory, there may be an overhead of copying data into physically contiguous memory before sending it to the preprocessing engine.
Another useful feature of the vvas_xinfer plug-in is its ability to consolidate the inferencing results of different stages of cascaded inferencing use cases. The plug-in can update/append the new metadata information generated at each stage into the metadata of the previous stages.
For implementation details, please refer to vvas_xinfer source code
Note
To ensure smooth operation of multithreaded applications, it is important to create the ML pipeline in such a way that vvas_xinfer instances are sequentially created instead of concurrently by multiple threads.
Input and Output¶
ML hardware engine supports images in BGR/RGB formats only (depending on model). Though this plug-in can accepts buffers with GRAY8, NV12, BGR, RGB, YUY2, r210, v308, GRAY10_LE32, ABGR, ARGB color formats on input GstPad & output GstPad, actual formats supported may vary depending on the hardware design, and the color formats enabled in the hardware design.
In case there is
image_processingkernel in the design, then user may choose to use hardware accelerated pre-processing and/or color space conversion. Make sureimage_processingkernel supports the required color format.In case
image_processingkernel in not there in the design then the input image tovvas_xinferplug-in must be in BGR/RGB format (depending on the model requirements) otherwise the results are unexpected.
vvas_xinferattaches theGstInferenceMetametadata to the output GstBuffer.. For details about meta data, refer to VVAS Inference Metadata
Control Parameters¶
Property Name |
Type |
Range |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
infer-config |
String |
N/A |
Null |
Complete path, including file name, of the inference configuration JSON file |
preprocess-config |
String |
N/A |
Null |
Complete path, including file name, of the pre-processing kernels config JSON file |
attach-empty-metadata |
Boolean |
True/False |
True |
Flag to decide attaching empty metadata strucutre when there is no inference results available for the current image |
batch-timeout |
Unsigned Integer |
0 - UINT_MAX |
0 (No timeout) |
time (in milliseconds) to wait when batch is not full, before pushing batch of frames for inference |
infer-config json members¶
Json key |
Item |
Item description |
|---|---|---|
inference-level |
Description |
Inference level in cascaded inference use case. e.g. Object detection ML (level-1) followed by object classification (level-2) on detected objects |
Value type |
Integer |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Default value |
1 |
|
low-latency |
Description |
Parameter to enable/disable low-latency mode in vvas_xinfer and it is useful only when inference-level > 1. If enabled, then vvas_xinfer plug-in will not wait for batch-size frames to be accumulated to reduce latency. If disabled, inference engine can work at maximum throughput. |
Value type |
Boolean |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Default value |
false |
|
inference-max-queue |
Description |
Maximum number of input frames those can be queued inside the plug-in. When low-latency is disabled, vvas_xinfer plug-in will wait for inference-max-queue buffers until batch-size is accumulated |
Value type |
Integer |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Default value |
batch-size |
|
attach-ppe-outbuf |
Description |
Attaches output of preprocessing library to GstInferenceMeta to avoid redoing of the preprocessing if required. |
Value type |
Boolean |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Default value |
False |
|
kernel |
Description |
Kernel object provides information about an VVAS kernel library configuration and kernel library name |
Value type |
JSON Object |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
None |
|
Object Members |
members of kernel JSON object are mentioned below |
infer-config::kernel json members¶
JSON key |
Item |
Description |
|---|---|---|
config |
Description |
Inference kernel specific configuration |
Value type |
JSON object |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
None |
|
Object members |
Contains members specific to inference library. Members of config JSON object are mentioned below |
infer-config::config json members¶
Parameter |
Type |
Expected Values |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
model-name |
string |
resnet50 |
N/A |
Name string of the machine learning model to be executed. The name string should be same as the name of the directory available in model -path parameter file. If the name of the model ELF file is resnet50.elf, then the model-name is resnet50 in the JSON file. The ELF file present in the specified path model-path of the JSON file. |
model-class |
string |
YOLOV3 FACEDETECT CLASSIFICATION SSD REFINEDET TFSSD YOLOV2 VEHICLECLASSIFICATION REID SEGMENTATION PLATEDETECT PLATENUM POSEDETECT BCC EFFICIENTDETD2 FACEFEATURE FACELANDMARK ROADLINE ULTRAFAST RAWTENSOR |
N/A |
Class of some model corresponding to model. Some examples are shown below:
|
model-format |
string |
RGB/BGR |
N/A |
Image color format required by model. |
model-path |
string |
|
N/A |
Path of the folder where the model to be executed is stored. |
vitis-ai-preprocess |
Boolean |
True/False |
True |
If vitis-ai-preprocess = true: Normalize with mean/scale through the Vitis AI Library If vitis-ai-preprocess = false: Normalize with mean/scale is performed before calling the vvas_xdpuinfer API’s. The Vitis AI library does not perform these operations. |
batch-size |
Integer |
0 to UINT_MAX |
N/A |
Number of frames to be processed in a single batch. If not set or set to zero or is greater than the batch-size supported by model, it is adjusted to the maximum batch-size supported by the model. |
float-feature |
Boolean |
True/False |
False |
This is used for FACEFEATURE class. If float-feature = true: Features are provided as float numbers. If float-feature = false: Features are provided as integers. |
max-objects |
Integer |
0 to UINT_MAX |
UINT_MAX |
Maximum number of objects to be detected. |
segoutfactor |
Integer |
0 to UINT_MAX |
1 |
Multiplication factor for Y8 output to look bright. |
seg-out-format |
string |
BGR/GRAY8 |
N/A |
Output color format of segmentation. |
filter-labels |
Array |
N/A |
Array of comma separated strings to filter objects with certain labels only. |
|
performance-test |
Boolean |
True/False |
False |
Enable performance test and corresponding flops per second (f/s) display logs. Calculates and displays the f/s of the standalone DPU after every second. |
postprocess-lib-path |
string |
/usr/lib/libvvascore_postprocessor.so |
N/A |
Library to post-process tensors. Absolute path of the library has to be given Embedded: /usr/lib/libvvascore_postprocessor.so PCIe: /opt/xilinx/vvas/lib/libvvascore_postprocessor.so |
debug-level |
Integer |
0 to 3 |
1 |
Used to enable log levels. There are four log levels for a message sent by the kernel library code, starting from level 0 and decreasing in severity till level 3 the lowest log-level identifier. When a log level is set, it acts as a filter, where only messages with a log-level lower than it, (therefore messages with an higher severity) are displayed. 0: This is the highest level in order of severity: it is used for messages about critical errors, both hardware and software related. 1: This level is used in situations where you attention is immediately required. 2: This is the log level used for information messages about the action performed by the kernel and output of model. 3: This level is used for debugging. |
preprocess-config json members¶
Table 4 preprocess-config json members
Json key |
Item |
Item description |
|---|---|---|
xclbin-location |
Description |
Location of xclbin which contains scaler IP to program FPGA device based on device-index property |
Value type |
String |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
NULL |
|
device-index |
Description |
Device index on which scaler IP is present |
Value type |
Integer |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory in PCIe platforms In embedded platforms, device-index is not an applicable option as it is always zero For software-ppe, device-index should be set to -1 |
|
Default value |
-1 in PCIe platforms 0 in Embedded platforms |
|
software-ppe |
Description |
Use software/hardware pre-processing. |
Value type |
Boolean |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Default value |
FALSE |
|
scaler-type |
Description |
Type of scaling to be used for resize operation. Some models require resize to be done with aspect-ratio preserved. If not set, default resizing will be done.
|
Value type |
string |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Expected Values |
letterbox/envelope_cropped |
|
Default value |
none |
|
scaler-horz-align |
Description |
Used when “scaler-type” = letterbox:
|
Value type |
string |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Expected Values |
left/right/center |
|
Default value |
left |
|
scaler-vert-align |
Description |
Used when “scaler-type” = letterbox.
|
Value type |
string |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Expected Values |
top/bottom/center |
|
Default value |
top |
|
scaler-pad-value |
Description |
pixel value of the padded region in letterbox cropping. |
Value type |
Integer |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Optional |
|
Expected Values |
0 - UINT_MAX |
|
Default value |
0 |
|
kernel |
Description |
Kernel object provides information about an VVAS library configuration. |
Value type |
JSON Object |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
None |
|
Object Members |
members of kernel JSON object are mentioned below |
preprocess-config::kernel json members¶
Table 5: preprocess-config::kernel json members
JSON key |
Item |
Description |
|---|---|---|
kernel-name |
Description |
Name of the preprocessing kernel. Syntax : “<kernel_name>:<instance_name>” |
Value type |
String |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
NULL |
|
config |
Description |
preprocess kernel specific configuration |
Value type |
JSON object |
|
Mandatory/Optional |
Mandatory |
|
Default value |
None |
|
Object members |
Contains members specific to preprocess library |
preprocess-config::config json members¶
Parameter |
Type |
Expected Values |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ppc |
Integer |
2/4 |
PCIe : 4 Embedded : 2 |
Pixel per clock supported by a multi- scaler kernel |
in-mem-bank |
Integer |
0 - 65535 |
0 |
VVAS input memory bank to allocate memory. |
out-mem-bank |
Integer |
0 - 65535 |
0 |
VVAS output memory bank to allocate memory. |
Json file for Labels¶
As of today, the vvas_dpuinfer library need labels information from detection model to map label number from tensor to label string. The label number to label string is expected in label.json file inner model directory of respective running model. The sample format of label.json is
{
"model-name": "yolov3_voc_tf",
"num-labels": 3,
"labels" :[
{
"name": "aeroplane",
"label": 0,
"display_name" : "aeroplane"
},
{
"name": "bicycle",
"label": 1,
"display_name" : "bicycle"
},
{
"name": "bird",
"label": 2,
"display_name" : "bird"
}
]
}
Note
Here “label” and “display_name” crossponds to number in models output tensor and string to be used for display purpose for the label, respectively.
Its is the user responsibility to provide the label.json file for his respected model if required.
Scaler Types¶
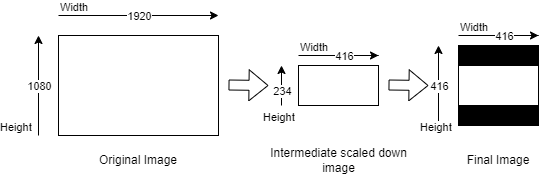
Letterbox¶
The letterbox scaling technique is used to maintain the aspect ratio of an image while resizing it to a specific resolution. This method involves determining the target aspect ratio and scaling the image down to fit within that ratio while preserving its original aspect ratio. The resulting image will have bars (either on the top and bottom or left and right) to fill in the remaining space, allowing the entire image to be visible without cutting off important parts.
For instance, consider an input image of 1920x1080 which needs to be resized to a resolution of 416x234 while preserving the aspect ratio. After resizing, the letterbox method is applied by adding black bars horizontally to the image, resulting in a final resolution of 416x416 pixels.
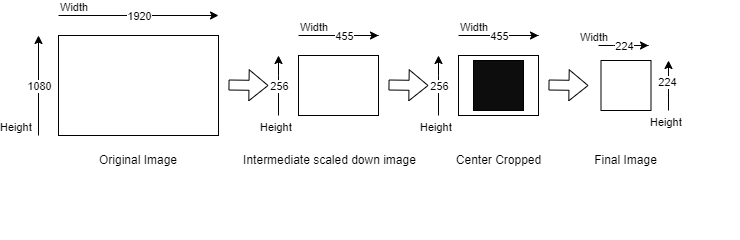
Envelope Cropped¶
Envelope cropped scaling is a digital image processing technique that resizes an image to fit a specific resolution while maintaining its aspect ratio. The algorithm involves several steps:
First, the target aspect ratio is determined by comparing the aspect ratio of the original image to that of the target resolution. Next, the image is scaled down by a factor that preserves its original aspect ratio while ensuring that the smallest side of the image fits within the target resolution. Finally, the image is cropped by removing equal parts from both sides of the image, thereby retaining the central part of the image.
This technique ensures that the input image is resized while preserving its aspect ratio and fitting the target resolution by scaling the image down to ensure that the smallest side fits within the target resolution. However, it may result in cutting off important parts of the image, so the potential impact on the model’s performance must be carefully considered.
For example, consider an input image of size 1920x1080 being scaled down to a resolution of 455x256 using the smallest side factor of 256 pixels, which preserves the original image’s aspect ratio. Following this, a center crop of 224x224 pixels is taken from the scaled image to achieve a final resolution of 224x224 pixels.
Note
Not all models require the use of the scaler-type parameter. Some models have specific requirements for image resizing to achieve better inference results. Therefore, it is recommended to use the scaler-type parameter only when necessary, and leave it unset otherwise.
bcc uses letterbox scaler-type for re-sizing.
efficientnetd2 models use envelope_cropped scaler-type for re-sizing.
Note
Vitis-AI-Preprocess does not support color format conversion. Therefore, if “vitis-ai-preprocess” is set to true, it is the user’s responsibility to provide the frame in the format required by the model.
If “vitis-ai-preprocess” is set to false and no preprocess-config is provided, it is necessary to perform pre-processing operations such as normalization and scaling on the frame prior to feeding it to vvas_xinfer. Failure to do so may result in unexpected outcomes.
When “vitis-ai-preprocess” is set to true in the infer-config json and a preprocess-config json is also provided, VVAS performs pre-processing using hardware acceleration for improved performance.
Note
Set “device-index” = -1 and “kernel-name” = image_processing_sw:{image_processing_sw_1} when using software-ppe from VVAS.
Note
If tensors are needed instead of post-processed results, user can set “model-class” = “RAWTENSOR” in the infer-config json file.
Users have the option to implement their own post-processing to handle the tensors. For instance, the vvascore_postprocessor library serves as a demonstration of how to create a post-processing library. It should be noted that this is simply an example library for reference purposes, and is not optimized.
The
vvascore_postprocessorlibrary only supports yolov3_voc, yolov3_voc_tf, plate_num, densebox_320_320, resnet_v1_50_tf models.
Example Pipelines and Jsons¶
Single stage inference example¶
Below is an example of a simple inference pipeline using YOLOv3. The input for this pipeline is an NV12 YUV file (test.nv12):
The pipeline employs the yolov3_voc_tf model for ML inference. First, a 1920x1080 NV12 frame is fed into the vvas_xinfer plugin. The pre-processor then resizes the frame and converts the color format to RGB, which is required by the model. In addition, mean value subtraction and normalization operations are performed on the frame. The resized and pre-processed frame is then passed to the inference library, which generates the inference predictions. These predictions are then upscaled to the original resolution (1920x1080) and attached to the output buffer.
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=<test.nv12> ! videoparse width=1920 height=1080 format=nv12 ! \
vvas_xinfer preprocess-config=yolov_preproc.json infer-config=yolov3_voc_tf.json ! fakesink -v
{
"inference-level":1,
"inference-max-queue":30,
"attach-ppe-outbuf": false,
"low-latency":false,
"kernel" : {
"config": {
"batch-size":0,
"model-name" : "yolov3_voc_tf",
"model-class" : "YOLOV3",
"model-format" : "RGB",
"model-path" : "/usr/share/vitis_ai_library/models/",
"vitis-ai-preprocess" : false,
"performance-test" : false,
"debug-level" : 0
}
}
}
{
"xclbin-location":"/run/media/mmcblk0p1/dpu.xclbin",
"software-ppe": false,
"device-index": 0,
"kernel" : {
"kernel-name": "image_processing:{image_processing_1}",
"config": {
"ppc": 4
}
}
}
2-level inference example¶
An example cascade inference (YOLOv3+Resnet18) pipeline which takes NV12 YUV file (test.nv12) as input is described below:
Here the objects detected in level-1 are cropped using vvas_xabrscaler and fed to vascore_dpuinfer for further inference.
Refer to jsons in above example for level-1. jsons files for level-2 are provided below.
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=<test.nv12> ! videoparse width=1920 height=1080 format=nv12 ! \
vvas_xinfer preprocess-config=yolo_preproc.json infer-config=yolov3_voc_tf.json ! queue ! \
vvas_xinfer preprocess-config=resnet_preproc.json infer-config=resnet18.json ! fakesink -v
{
"inference-level":2,
"inference-max-queue":30,
"attach-ppe-outbuf": false,
"low-latency":false,
"kernel" : {
"config": {
"batch-size":0,
"model-name" : "resnet50",
"model-class" : "CLASSIFICATION",
"model-format" : "RGB",
"model-path" : "/usr/share/vitis_ai_library/models/",
"vitis-ai-preprocess" : false,
"performance-test" : false,
"debug-level" : 0
}
}
}
{
"xclbin-location":"/run/media/mmcblk0p1/dpu.xclbin",
"software-ppe": false,
"device-index": 0,
"kernel" : {
"kernel-name": "image_processing:{image_processing_1}",
"config": {
"ppc": 4
}
}
}
Rawtensor example¶
An example inference pipeline to get tensors is described below:
The below pipeline performs inference using yolov3_voc_tf model. In the infer-json model-class: RAWTENSOR indicates that tensors are required by the user instead of post-processed inference results.
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=<test.nv12> ! videoparse width=1920 height=1080 format=nv12 ! \
vvas_xinfer preprocess-config=yolo_preproc.json infer-config=yolov3_voc_tf.json ! fakesink -v
{
"inference-level":1,
"inference-max-queue":30,
"attach-ppe-outbuf": false,
"low-latency":false,
"kernel" : {
"config": {
"batch-size":0,
"model-name" : "yolov3_voc_tf",
"model-class" : "RAWTENSOR",
"model-format" : "RGB",
"model-path" : "/usr/share/vitis_ai_library/models/",
"vitis-ai-preprocess" : false,
"performance-test" : false,
"debug-level" : 0
}
}
}
{
"xclbin-location":"/run/media/mmcblk0p1/dpu.xclbin",
"software-ppe": false,
"device-index": 0,
"kernel" : {
"kernel-name": "image_processing:{image_processing_1}",
"config": {
"ppc": 4
}
}
}
Using the same pipeline described above, if post-processing has to be performed on the tensors, postprocess-lib-path is added in the infer-config json. Note that the post-processing library used here is only a refernce library and does not support all models.
{
"inference-level":1,
"inference-max-queue":30,
"attach-ppe-outbuf": false,
"low-latency":false,
"kernel" : {
"config": {
"batch-size":0,
"model-name" : "yolov3_voc_tf",
"model-class" : "RAWTENSOR",
"postprocess-lib-path" : "/opt/xilinx/vvas/lib/libvvascore_postprocessor.so",
"model-format" : "RGB",
"model-path" : "/usr/share/vitis_ai_library/models/",
"vitis-ai-preprocess" : false,
"performance-test" : false,
"debug-level" : 0
}
}
}